Overview
This chapter mainly introduces the composition of the programming interface and the functions of each module. If you already have a certain understanding of this, you can skip this chapter.
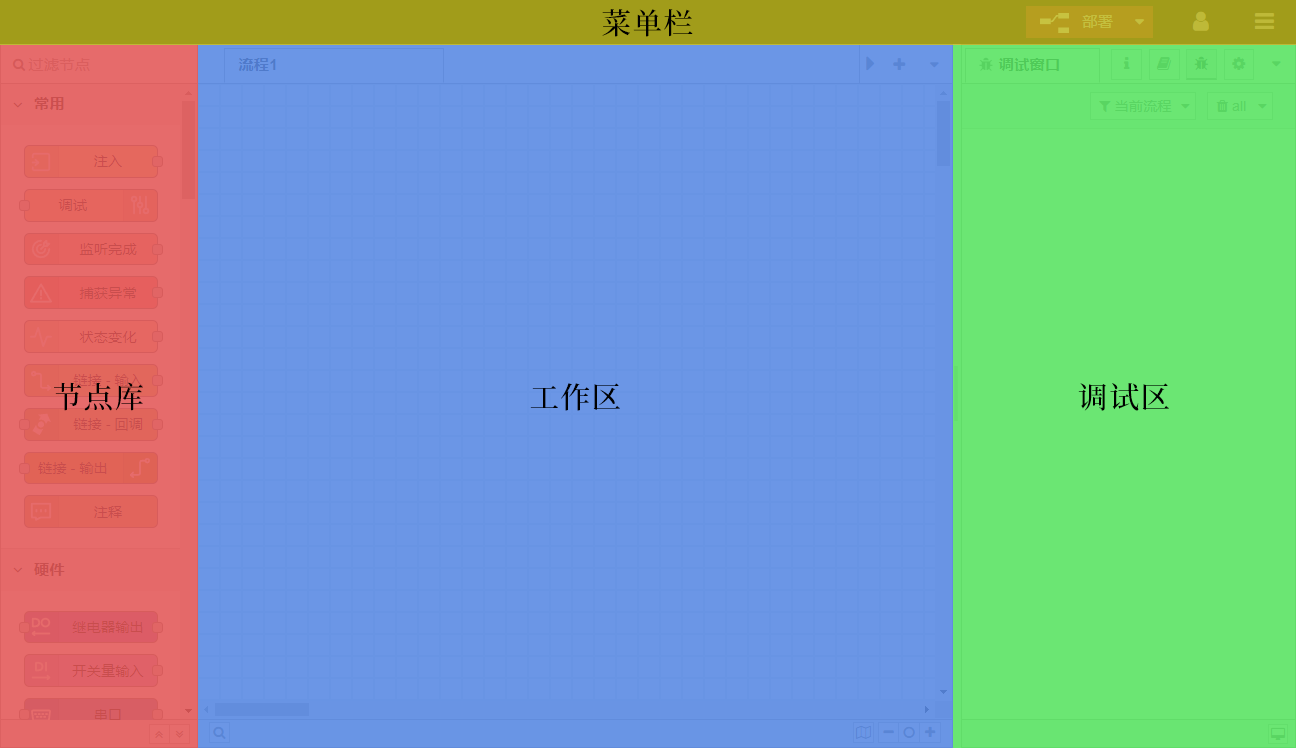
Menu bar: The menu bar at the top, including deployment buttons and main menu (process import and export are in the menu bar)
Node library: Provides various nodes with encapsulated functions for users to call
Workspace: Drag nodes into the workspace and connect them to represent data interaction to achieve free programming.
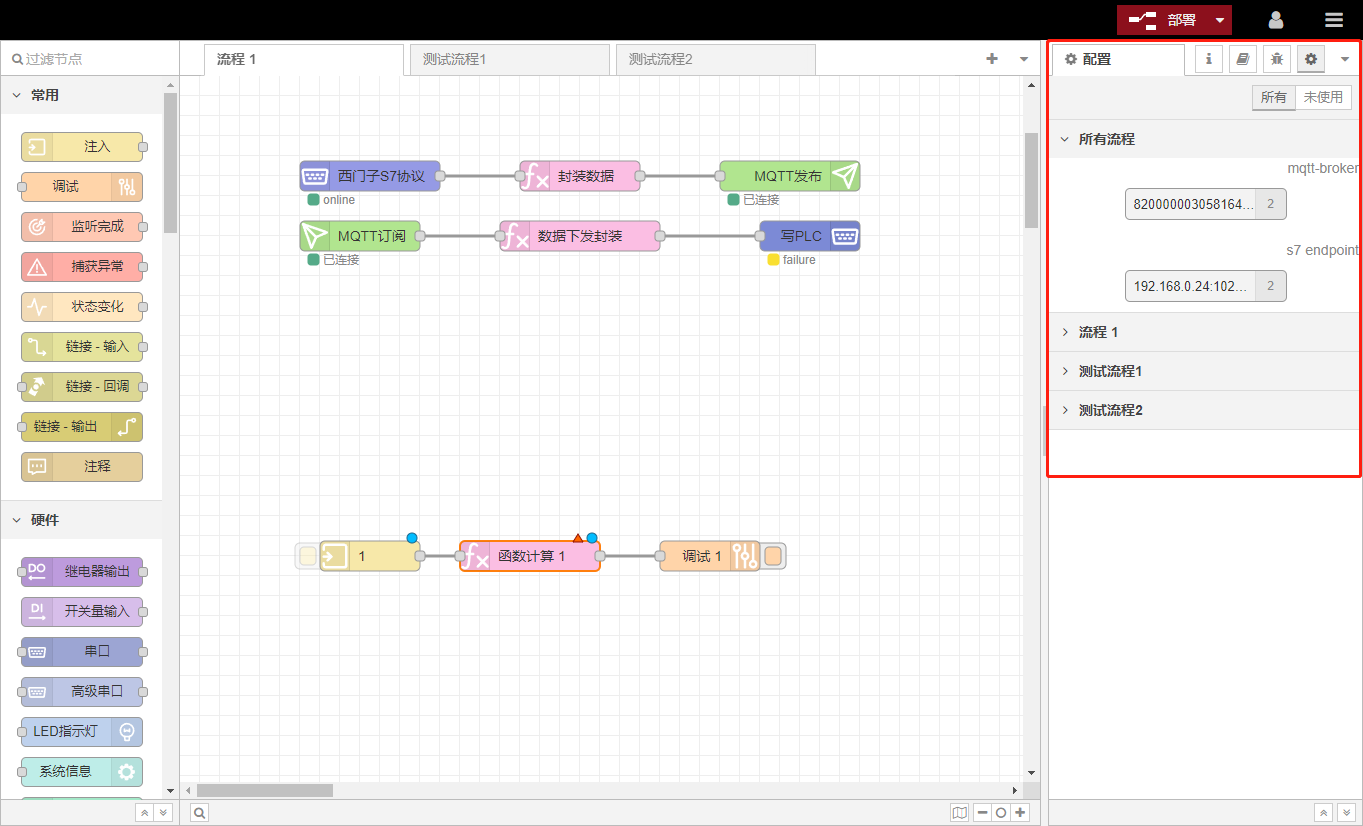
Debug area: divided into 5 pages, namely: 信息窗口/ 帮助文档/ 日志窗口/ 配置节点/ 全局变量
Menu Bar
1. Deployment
After the process development is completed, it only exists in the workspace and is not deployed on the gateway, so it will not be executed.To execute the process, you must click the deploy button after the process is completed to save the process in the gateway.
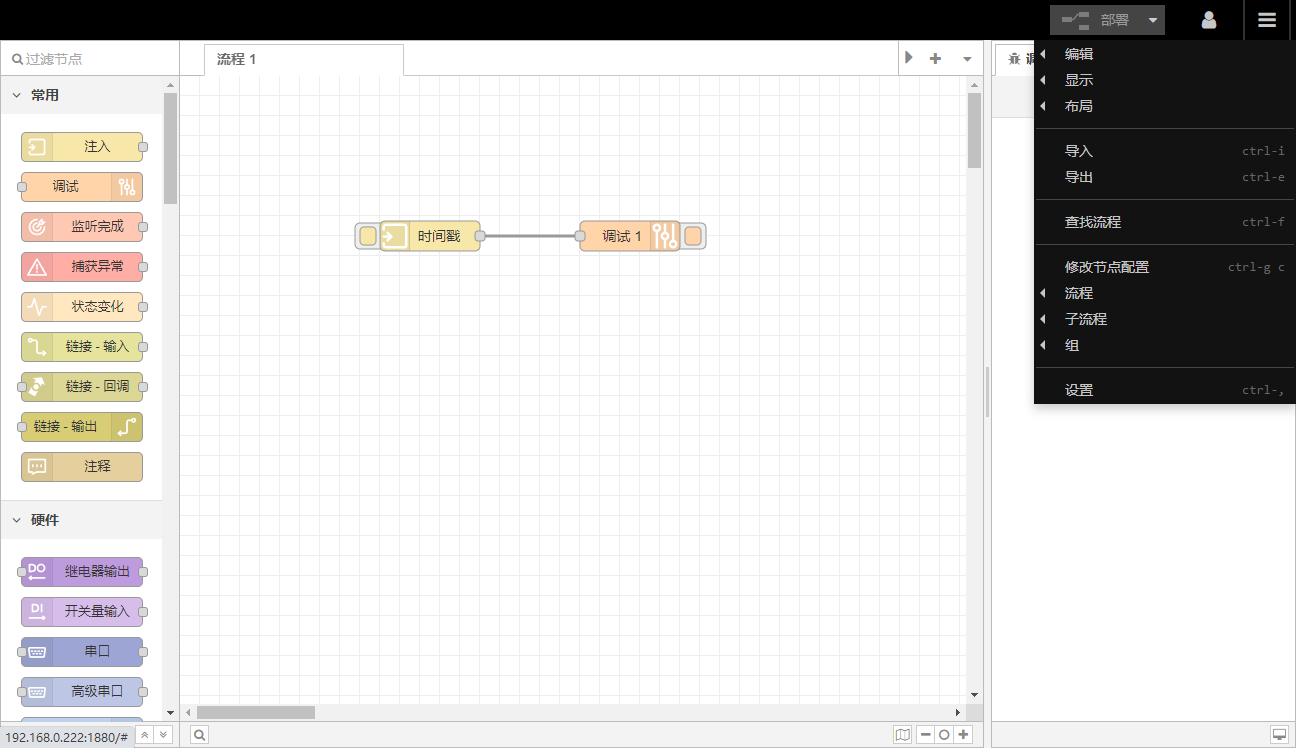
2.Menu _
The commonly used functions of the menu bar are import and export. The actual storage carrier of the process is a json file. After the process is completed, the process can be backed up through the export function. Similarly, if you need to deploy a completed process on a new gateway, you can use the import function.
node library
The node library contains all nodes that have been installed and can be used directly.
The node library is classified according to function, in order: common nodes, hardware nodes, function nodes, network nodes, sequence nodes, storage nodes, advanced nodes, and PLC nodes.Subsequent chapters will introduce the specific functions and usage of each node in turn.
Nodes form processes through connections, so nodes are the basic elements and core elements of the process. Whether you are proficient in the functions of each node determines the efficiency of the development process. The same needs can be achieved by different people using different nodes, and there is no fixed solution.Our mission is to continuously develop new nodes and continuously improve your work efficiency
workspace
1. Process
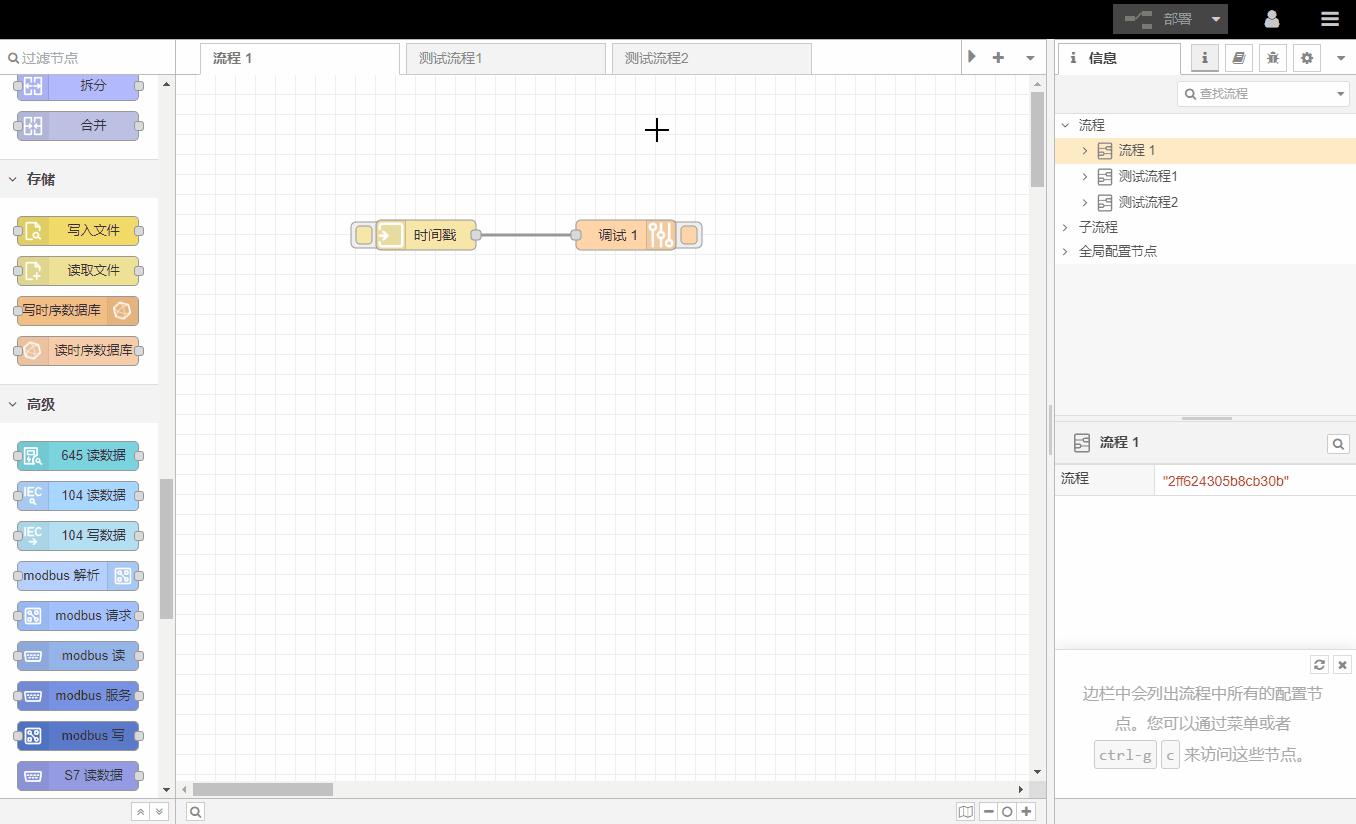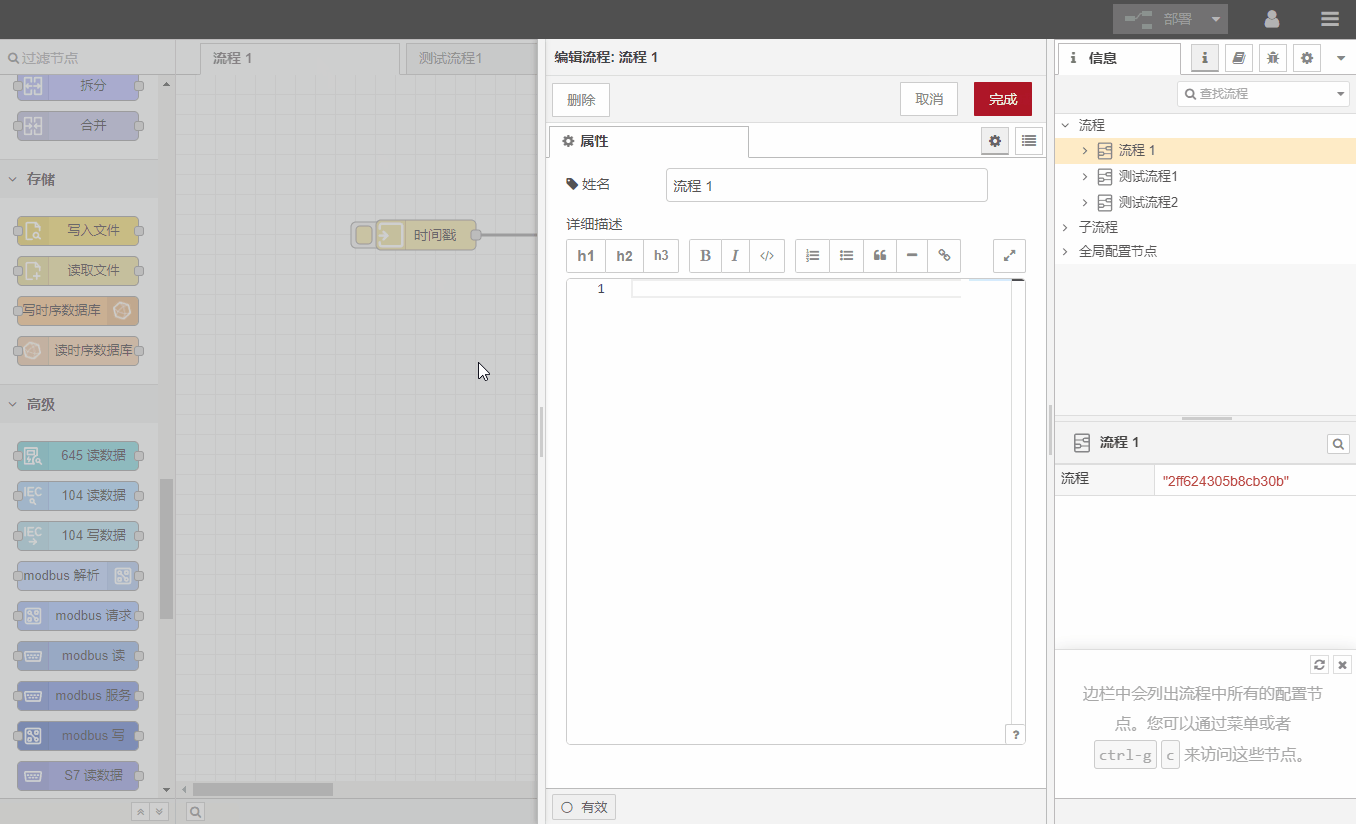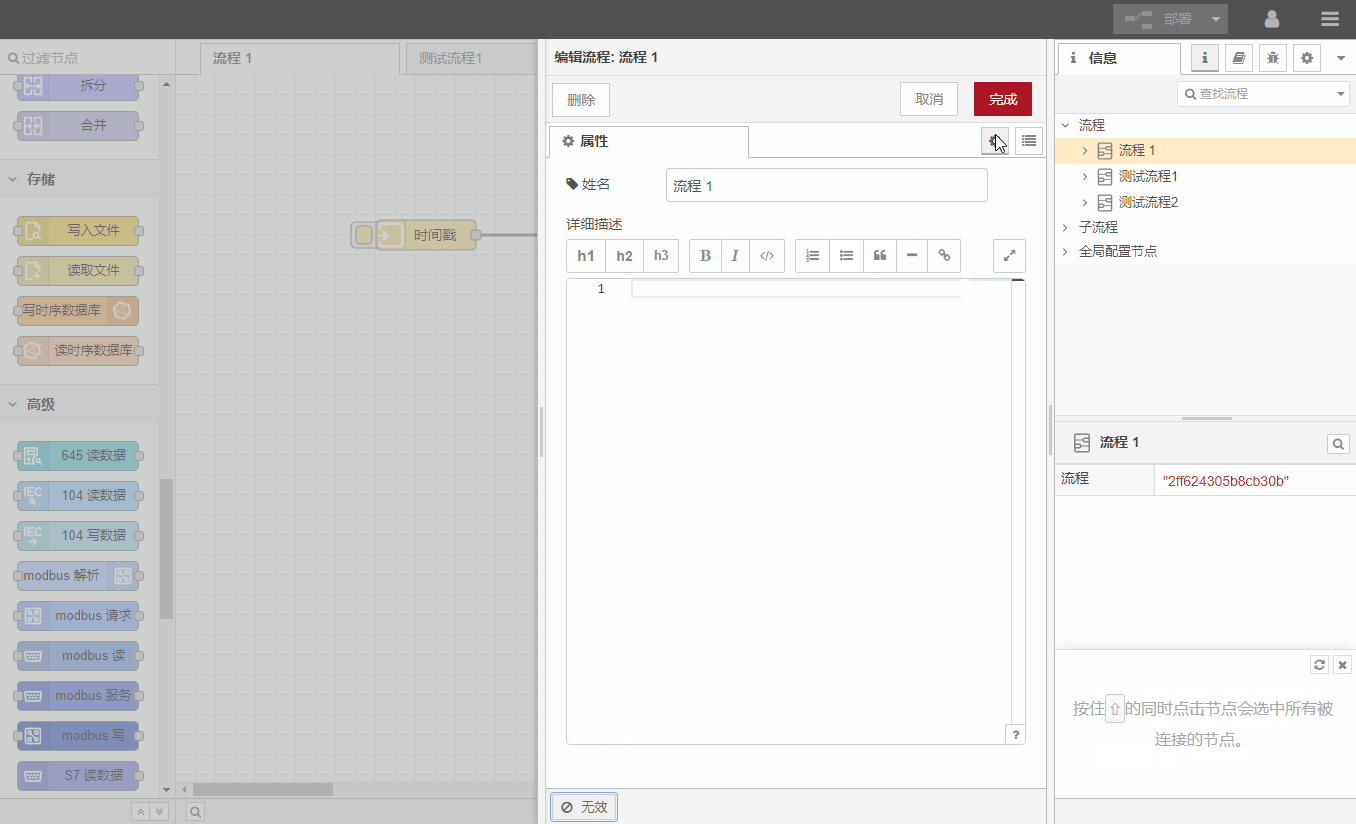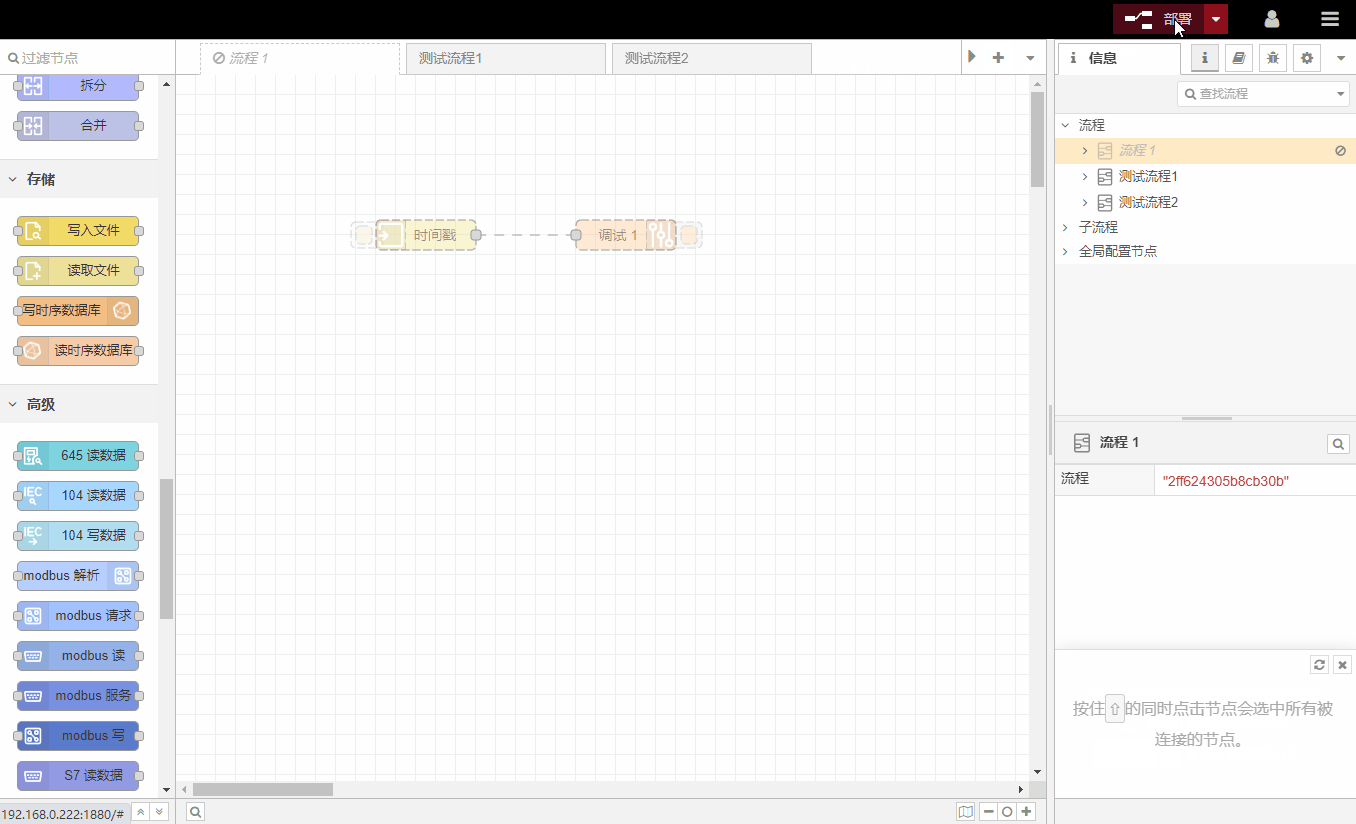
A process is a program that realizes your needs. Because the process of connecting nodes is the process of data transfer, the process is like water flow, so it is called a process . A process is a combination of nodes and lines. The process has no specific direction. You can call a program that implements a small function point a process, or you can call the entire project a process.In order to facilitate management, multiple tabs (process pages) can be created in the workspace, and individual tabs can be renamed to facilitate memory management.

To enable/disable/delete a process , double-click the process tab. There is a valid button in the lower left corner of the dialog box to control enabling or disabling the process. If disabled is selected, the process has no effect when deployed.There is a delete button in the upper left corner of the dialog box to delete the process.
2.Node _
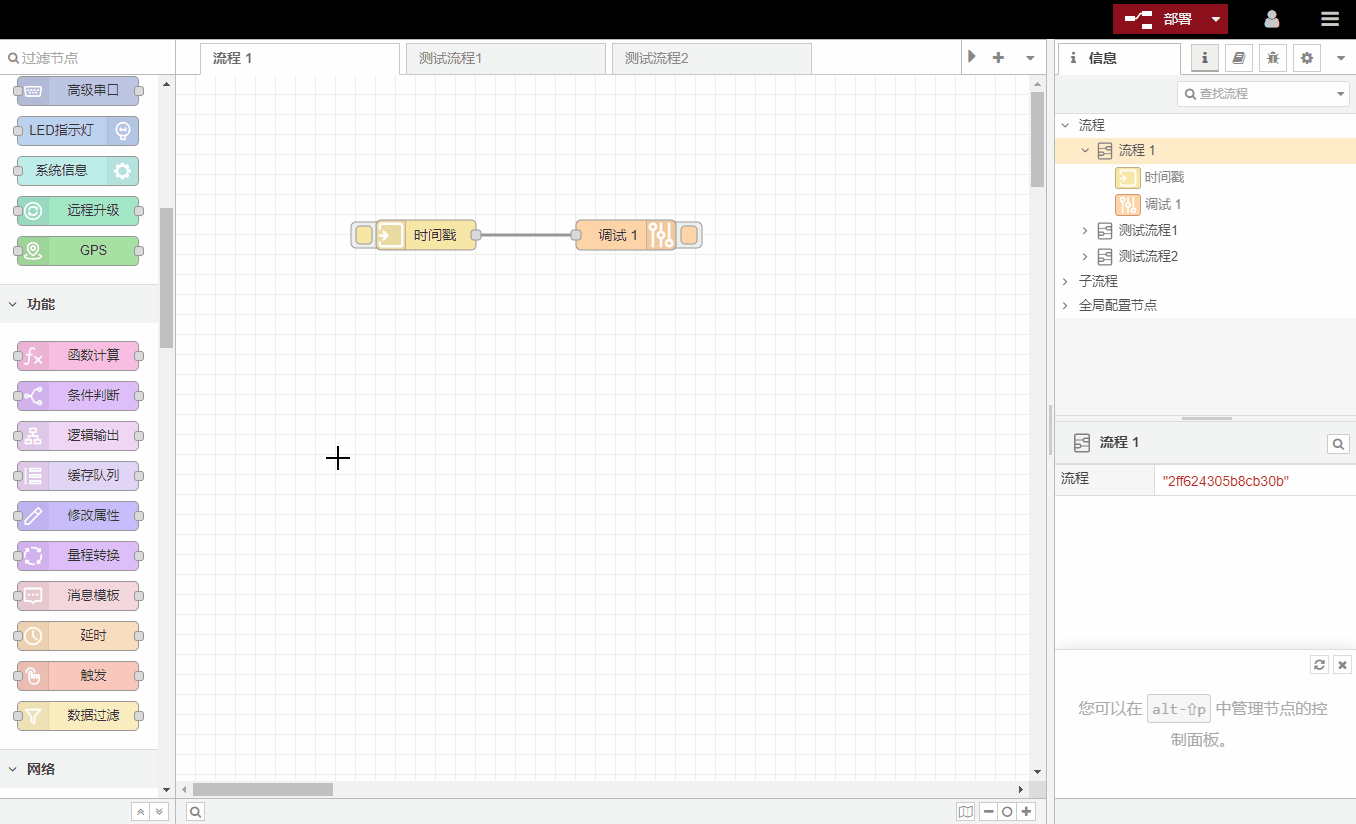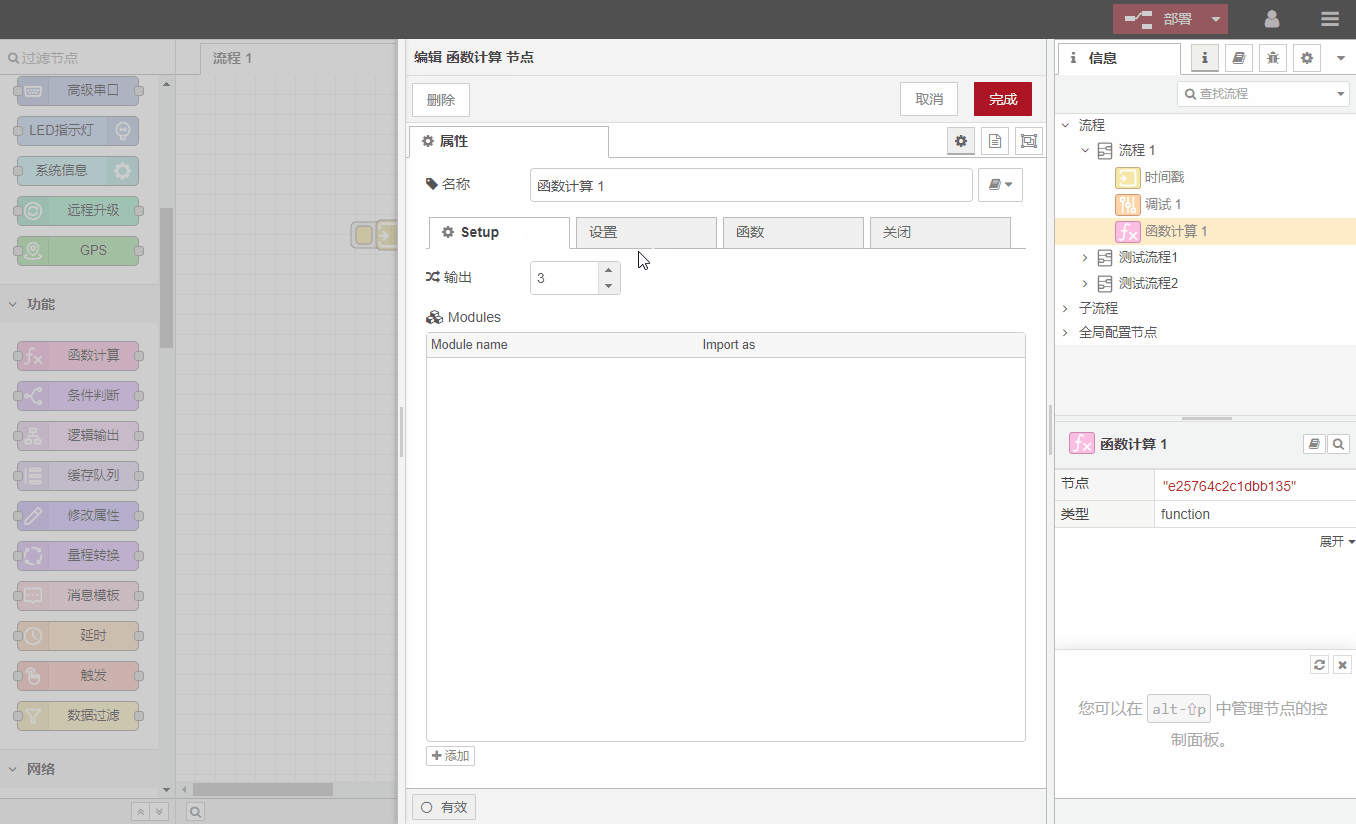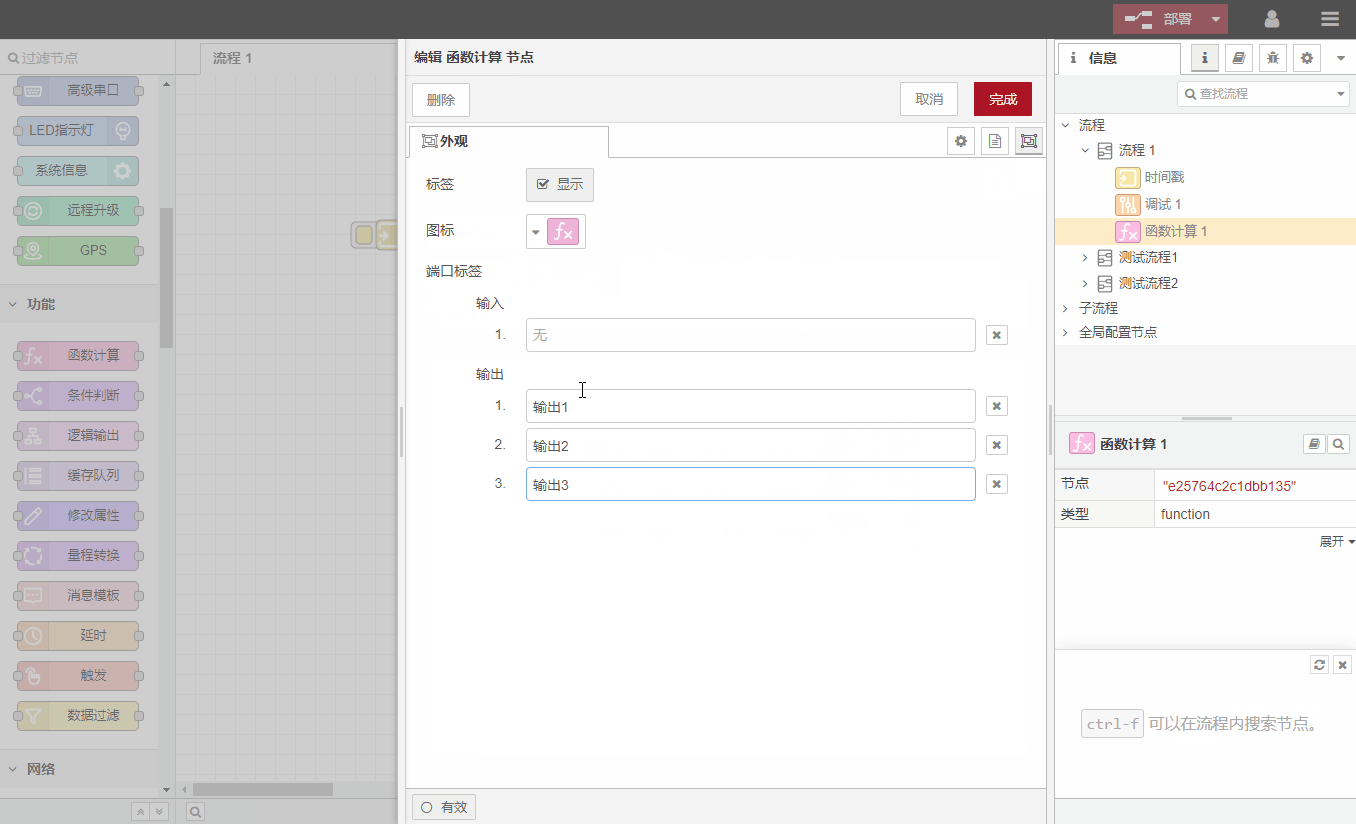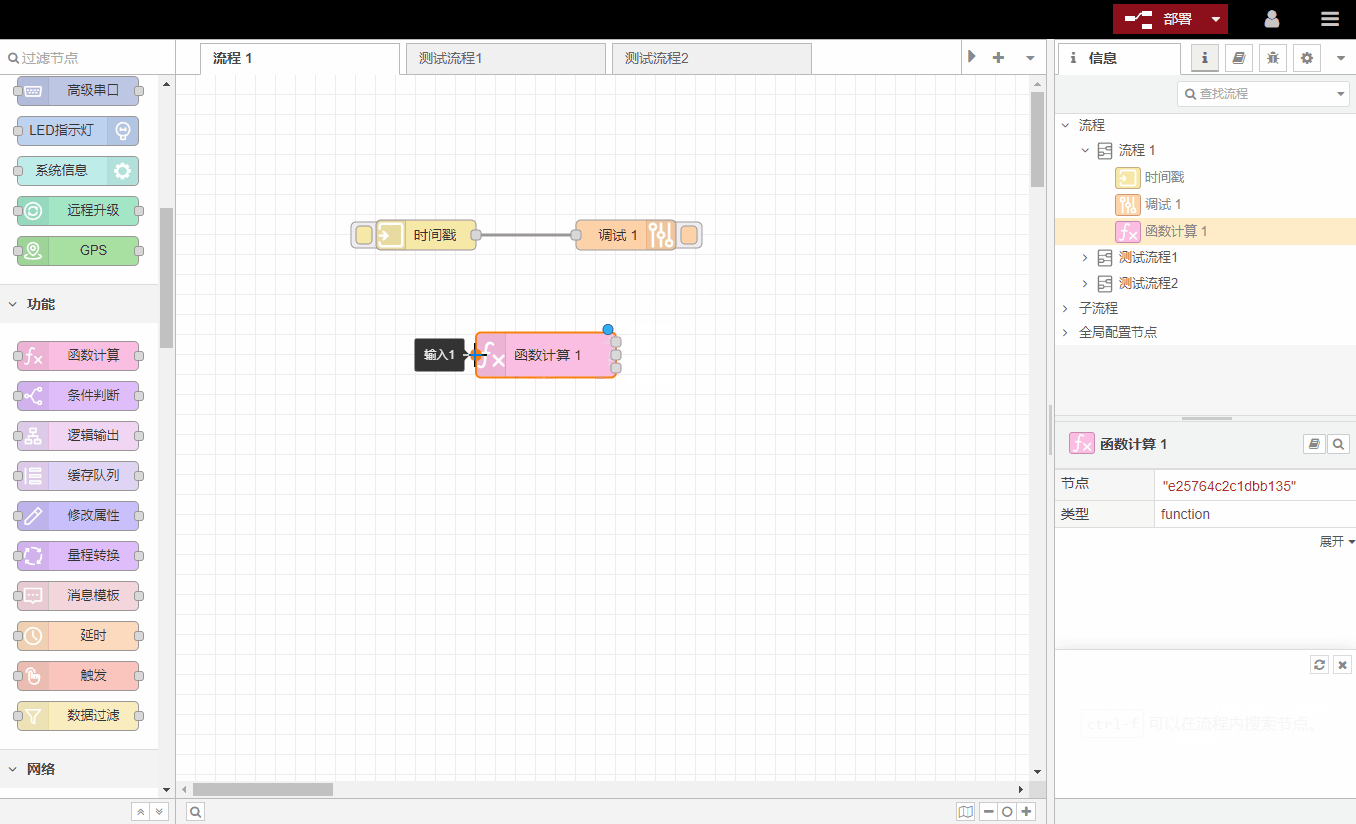
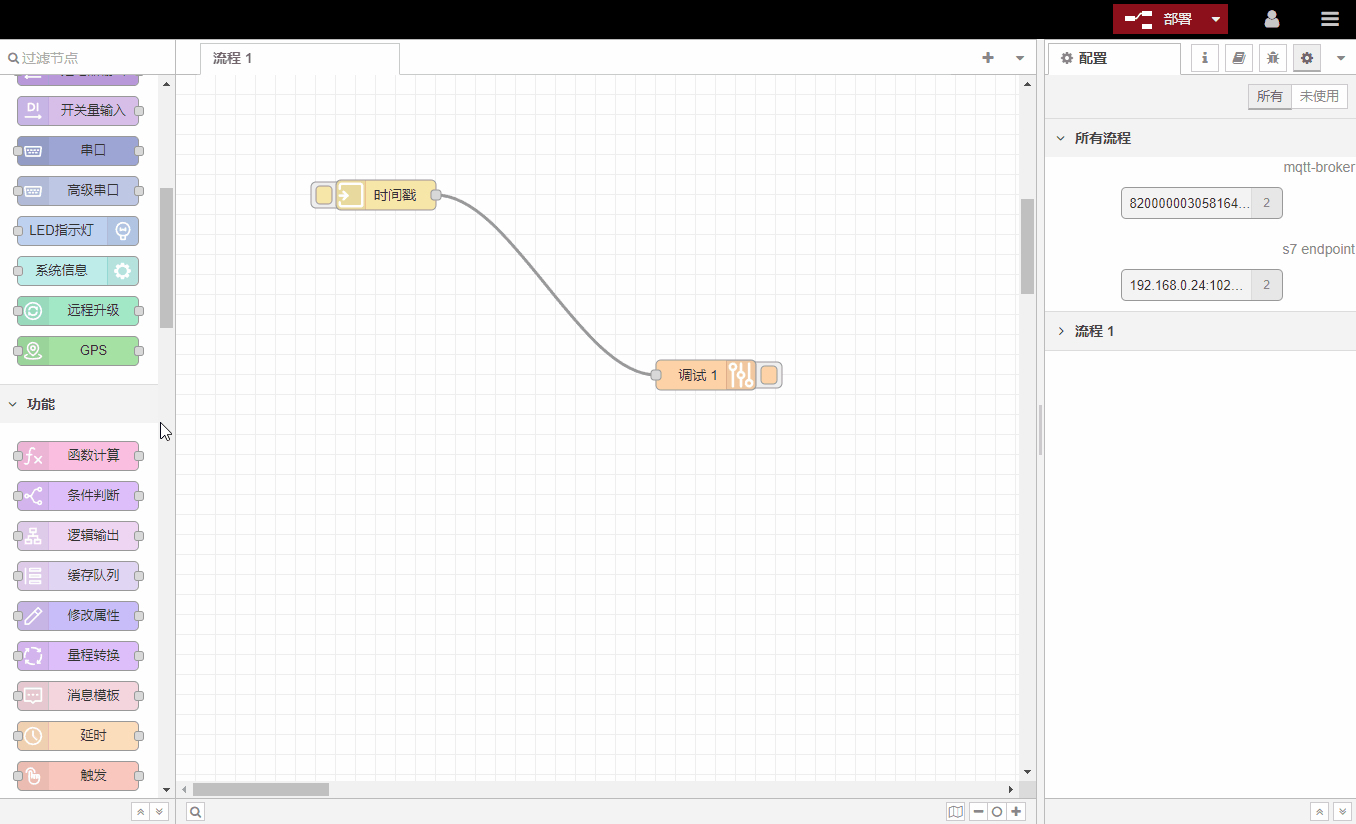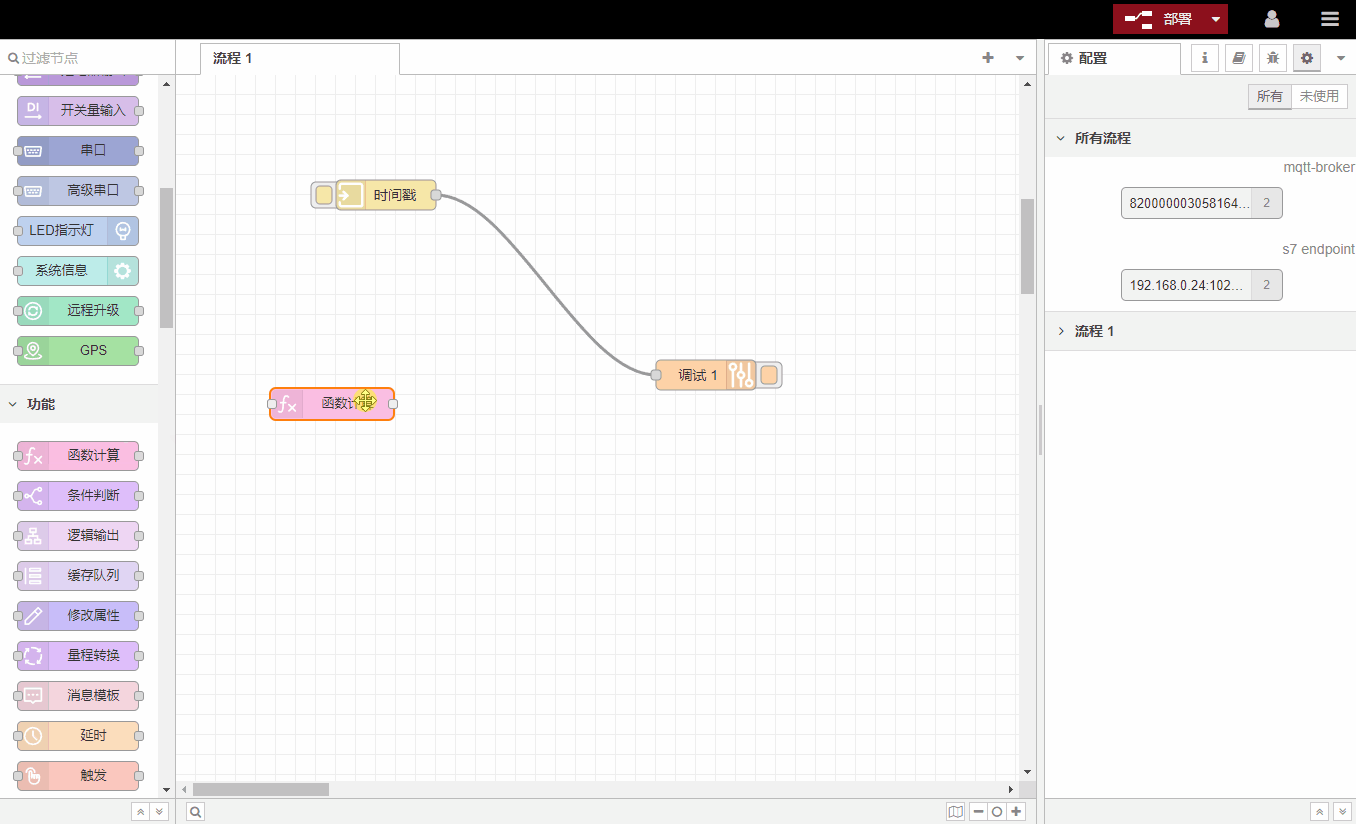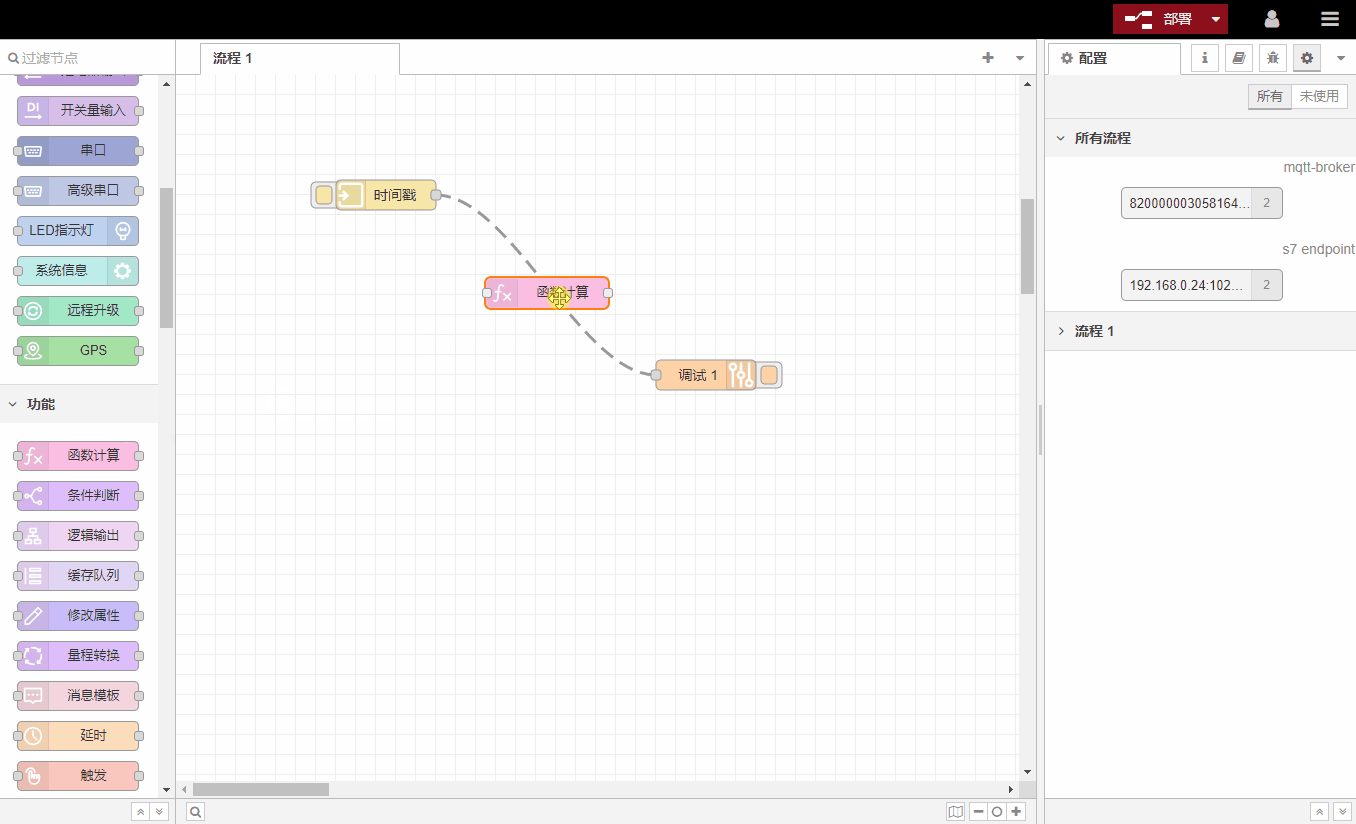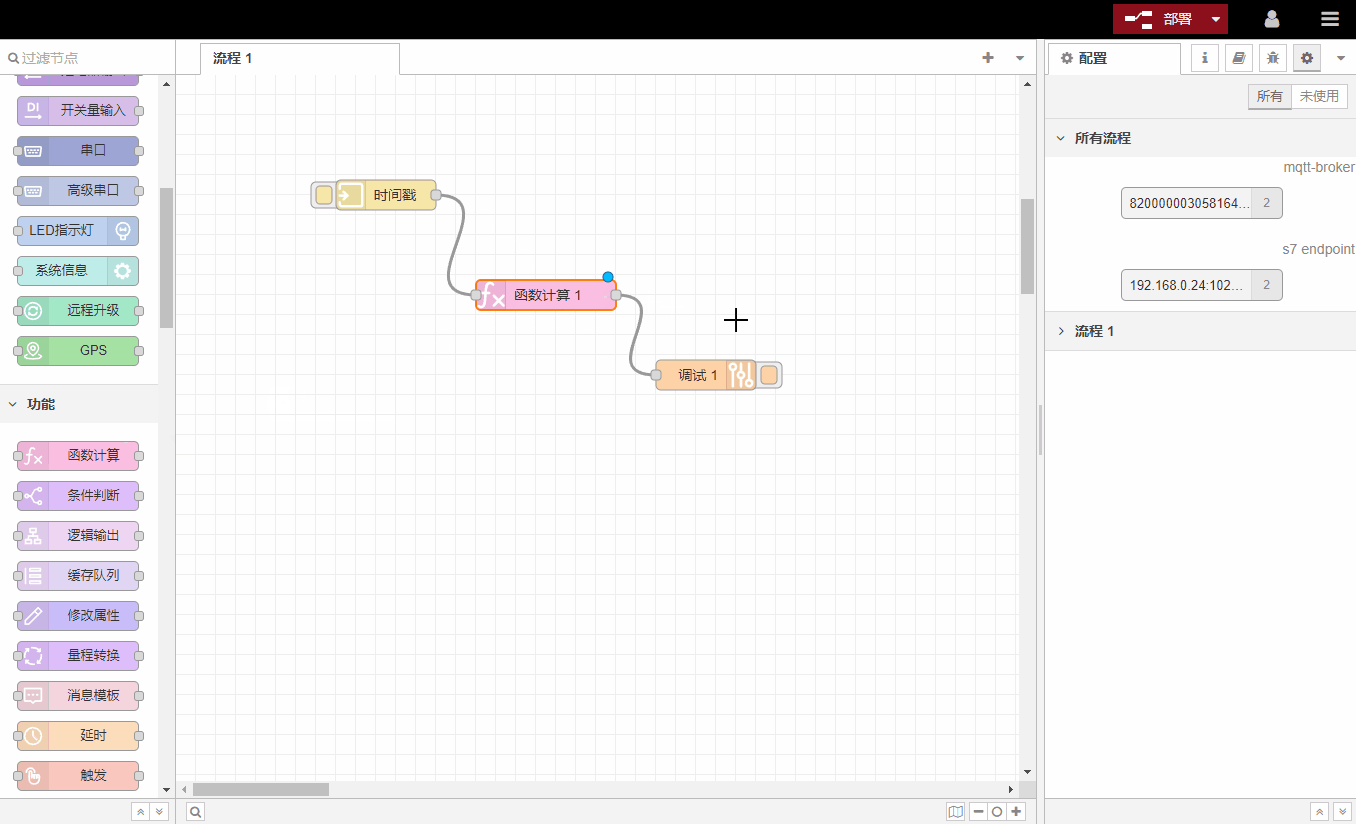
Nodes are connected together by lines. A node can have multiple input ports and multiple output ports (except for individual nodes, the number of input and output ports is predefined and cannot be modified). When the mouse is hovering over the port, the port will display a label. You can also define the label of the port yourself to facilitate memory, as shown in the figure:
Some nodes will display a status bar below to indicate the running status of the node. For example, the status bar of MQTT节点indicates the MQTT connection status:
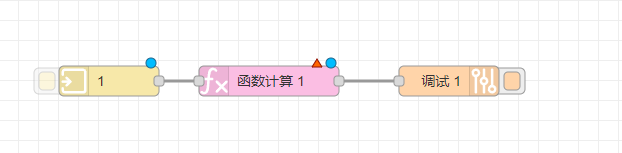
If the node has any undeployed modifications, a blue dot will be displayed in the upper right corner of the node, and if there are configuration errors, a red triangle will be displayed:
A configuration node is a special type of node that can share its configuration with other regular nodes. For example, both MQTT发布节点and MQTT订阅节点can use the same MQTT配置节点to indicate that they are using the same MQTT connection.The currently known configuration nodes of the gateway include: 串口配置节点, MQTT配置节点, and PLC配置节点. The configuration node is not visible in the work area. You can view the current process in the debugging area.
3.Connect _
If you drag a node with both input and output ports through the center of a connection, the existing connection will become a dotted line. Release the node at this time and the changed node will be automatically inserted into the original process.
Select the connection and press the Delete key to delete the connection
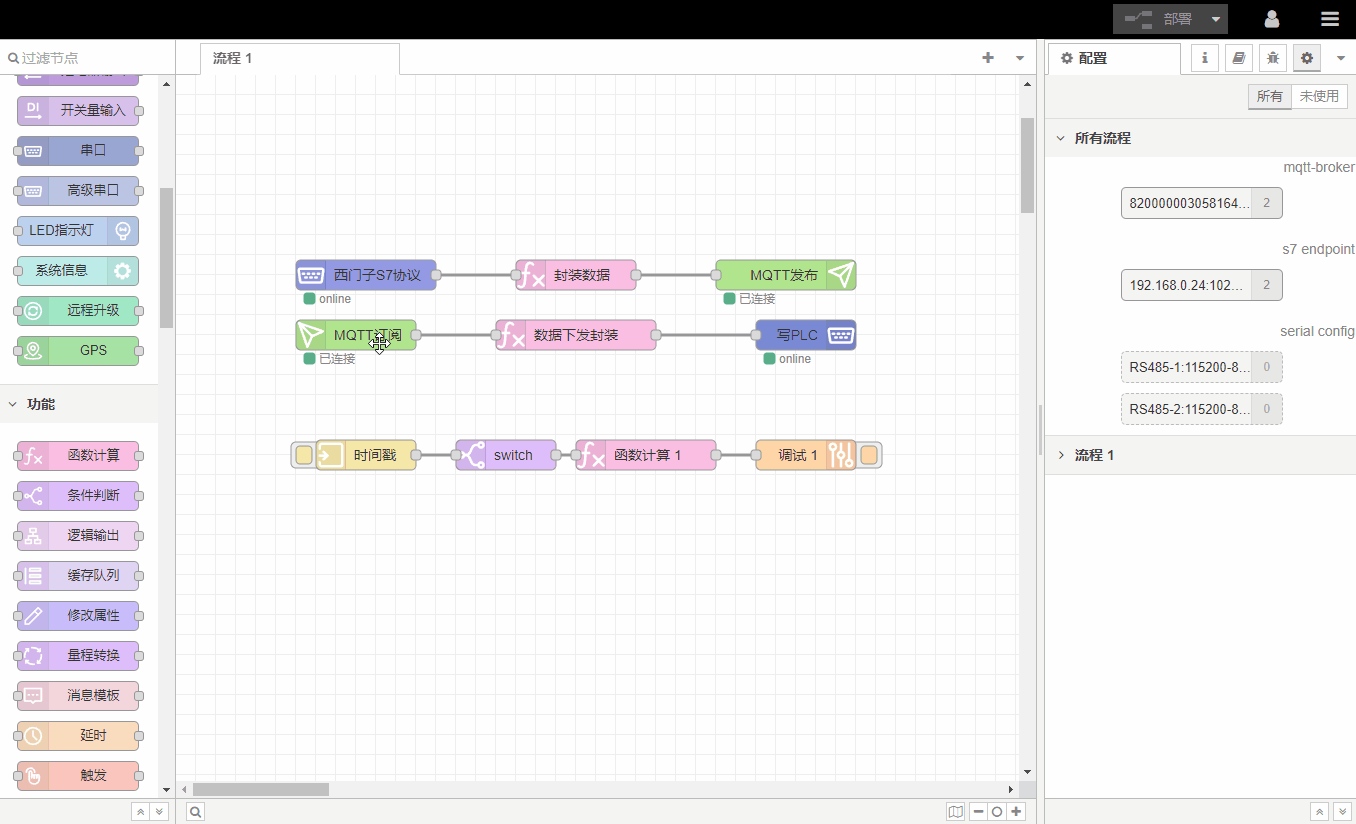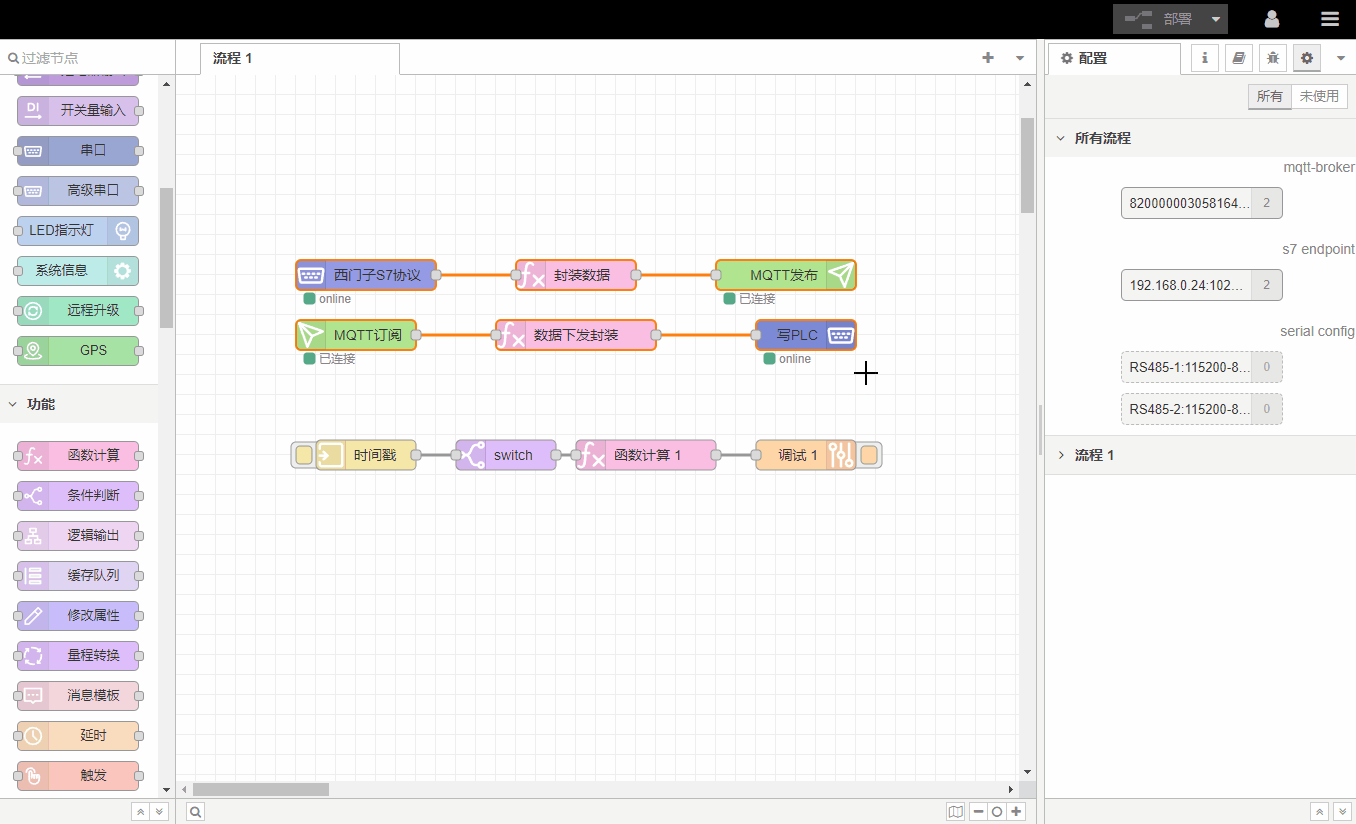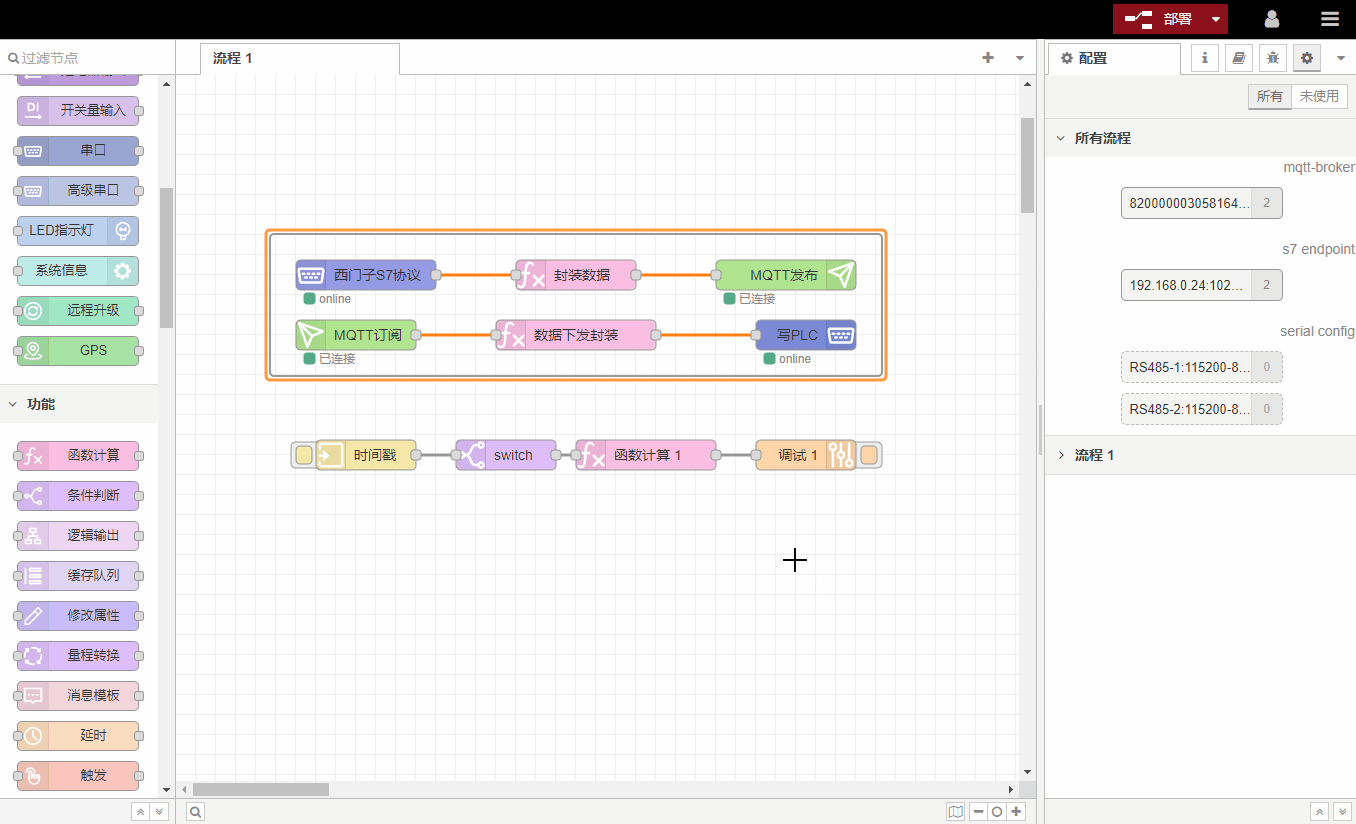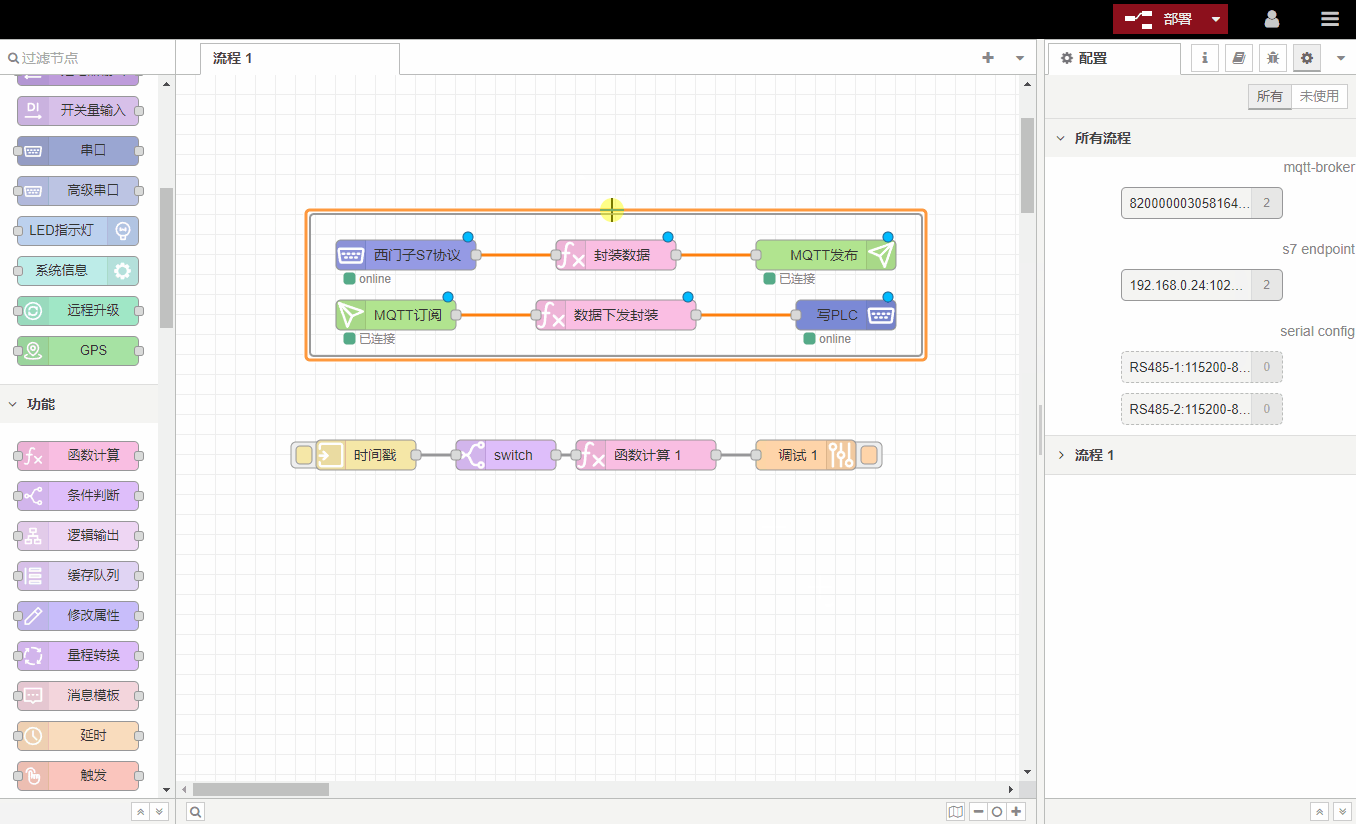
4. Create a group
Nodes can be connected together to form a group and then moved or copied as a single object in the workspace
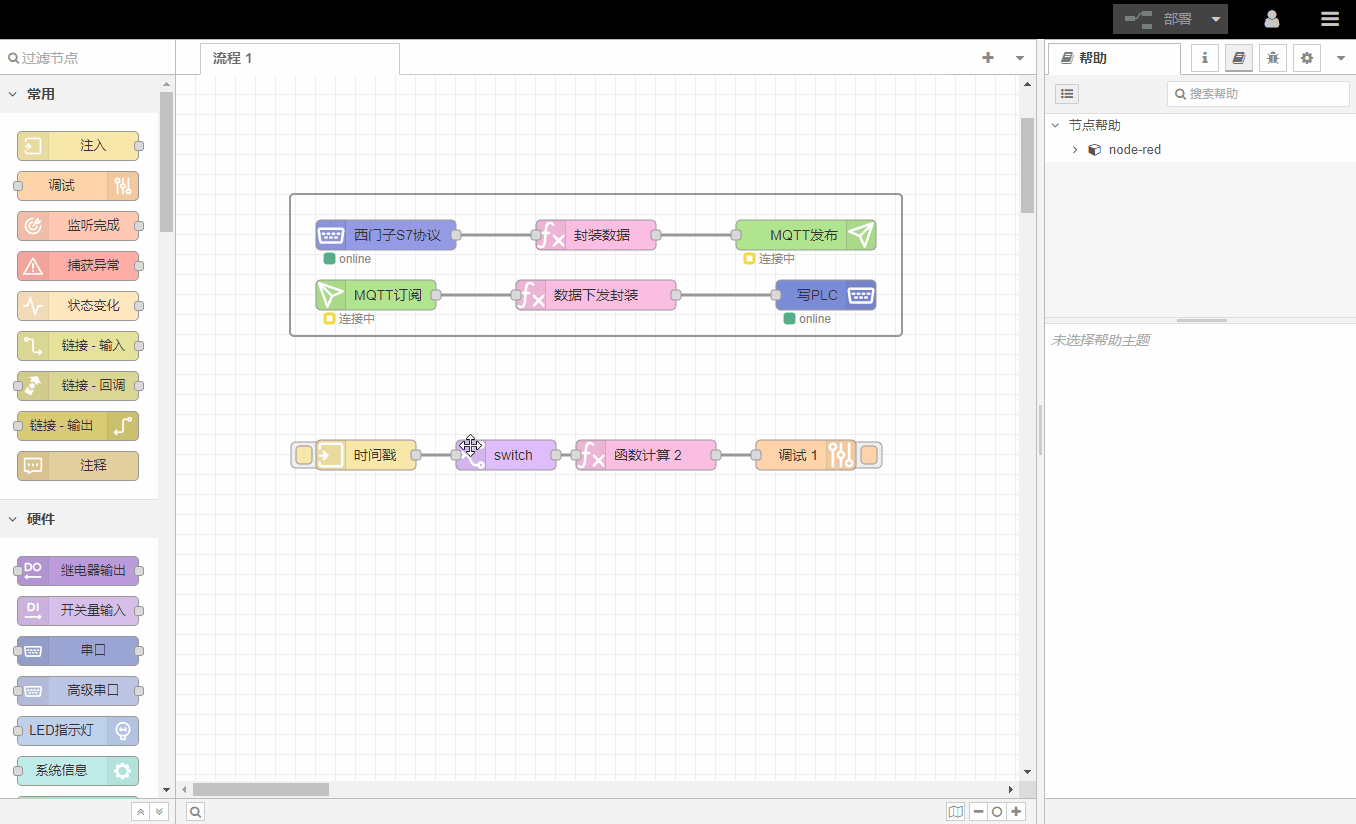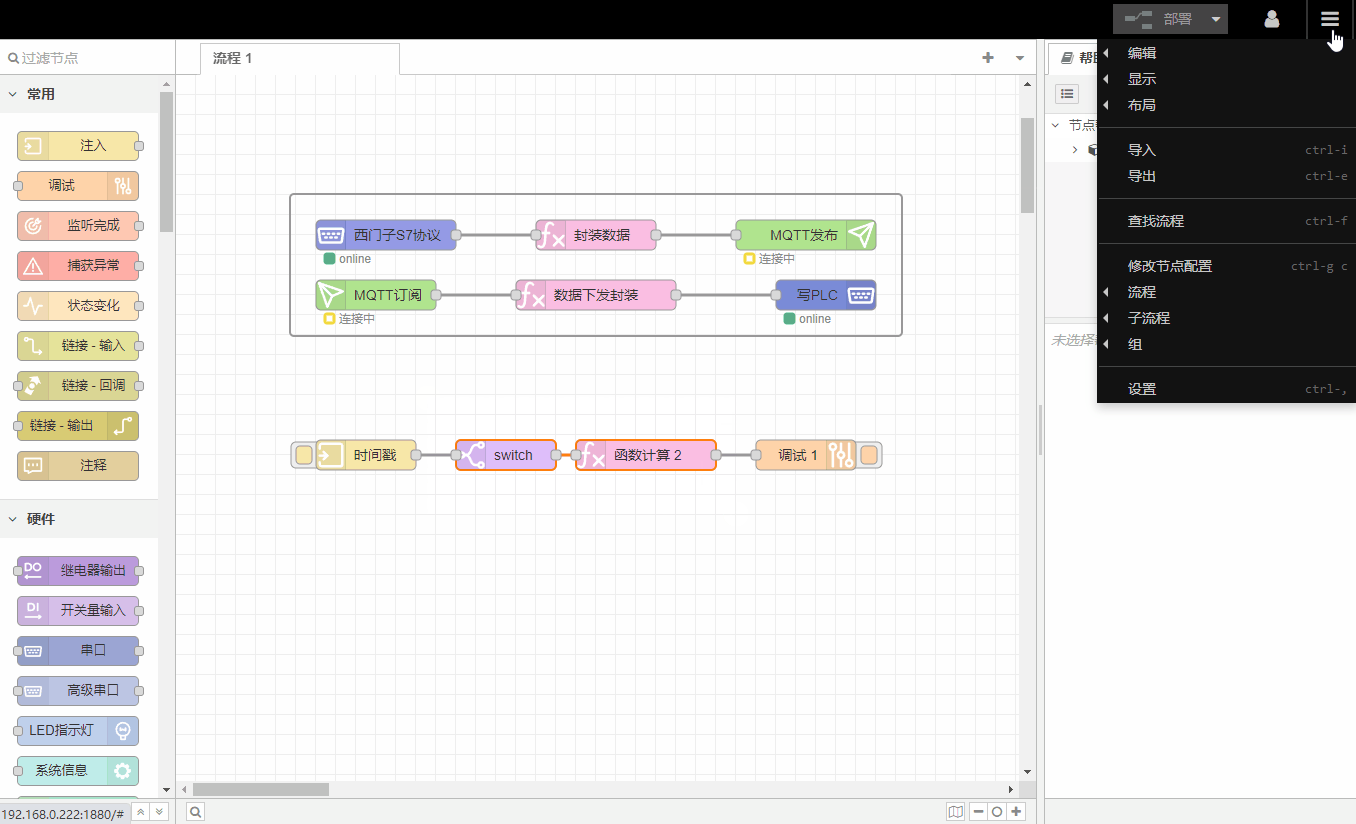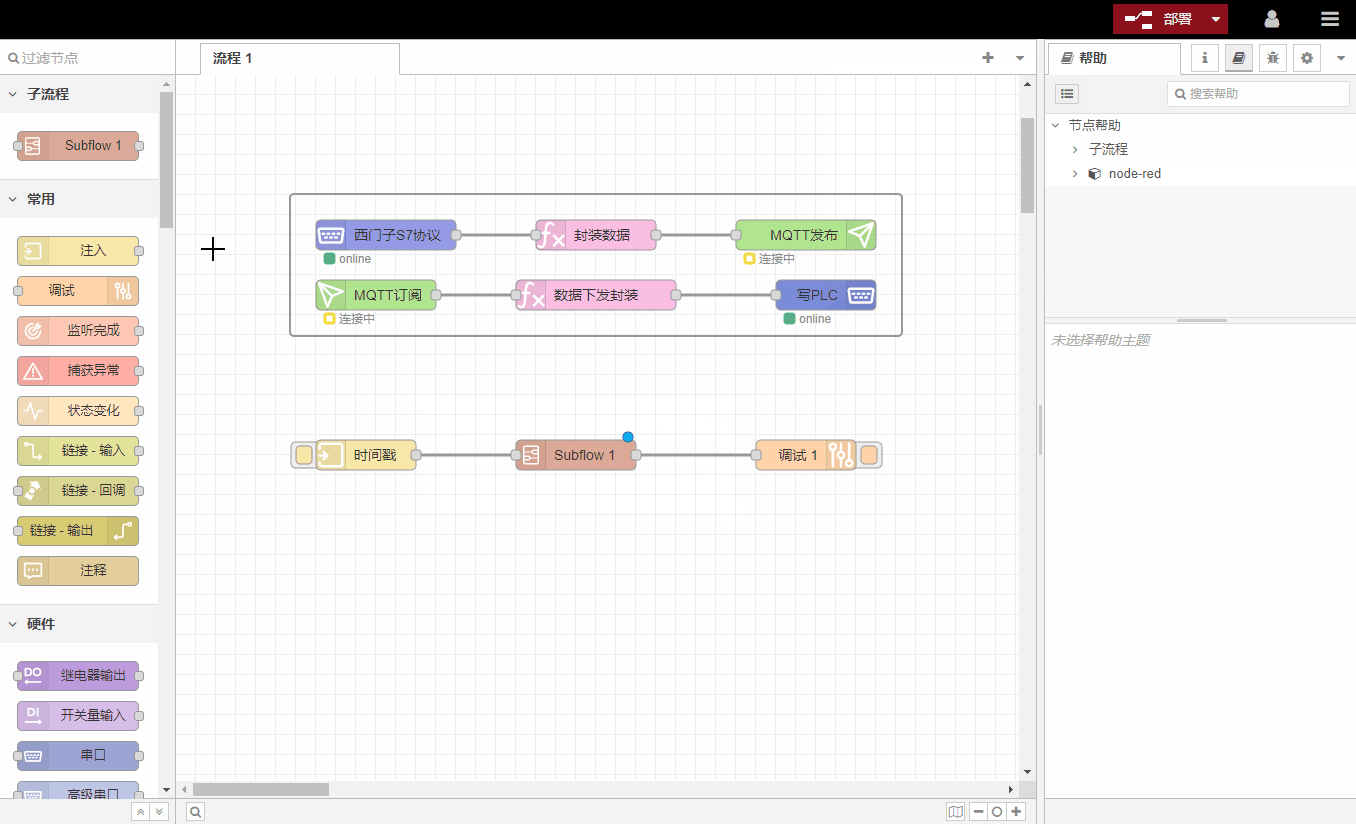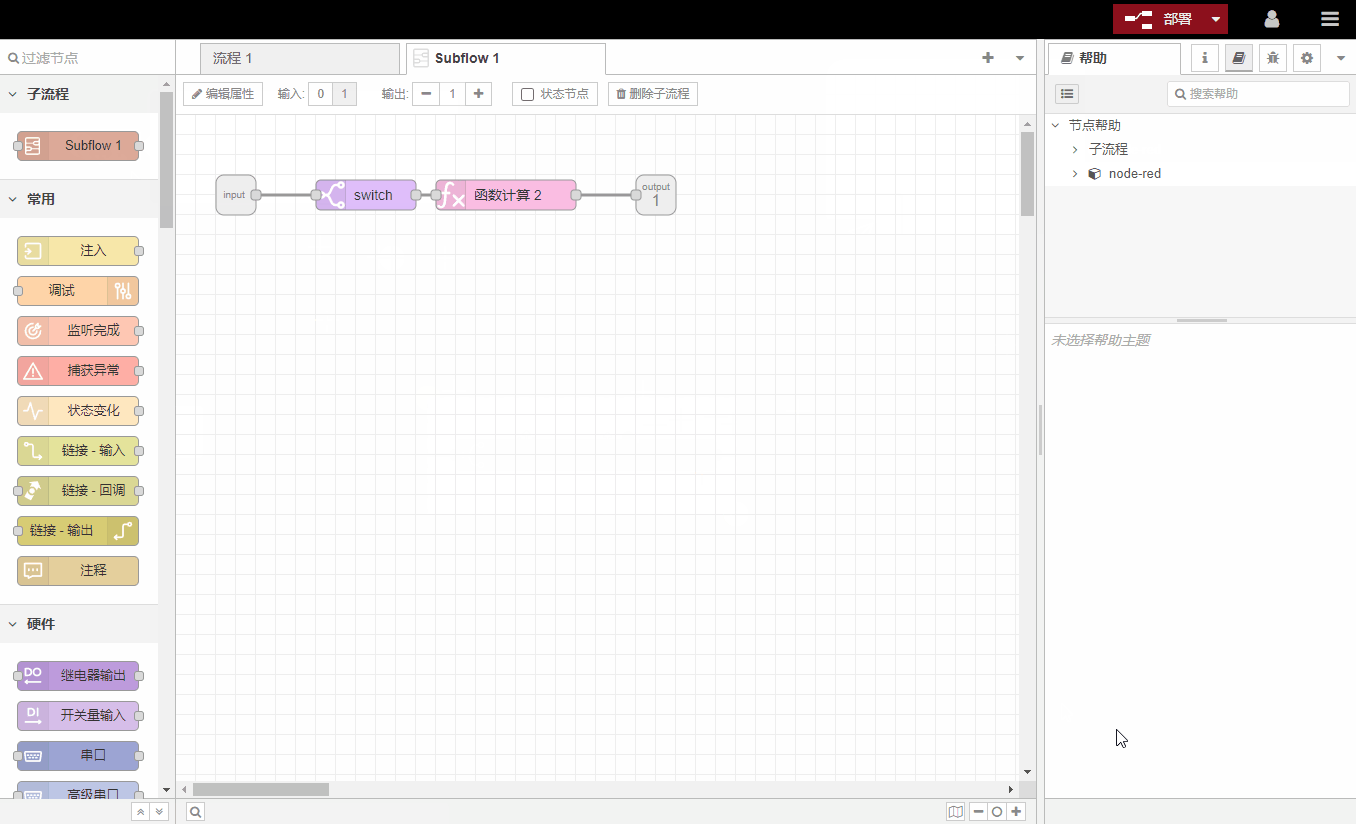
5.Sub -process
Some collections of nodes can be collapsed into a single node for use in the workspace. The collapsed node is called a subprocess.
Subprocesses can reduce the visual complexity of the process, or combine commonly used nodes into reusable flows.
6. Import and export
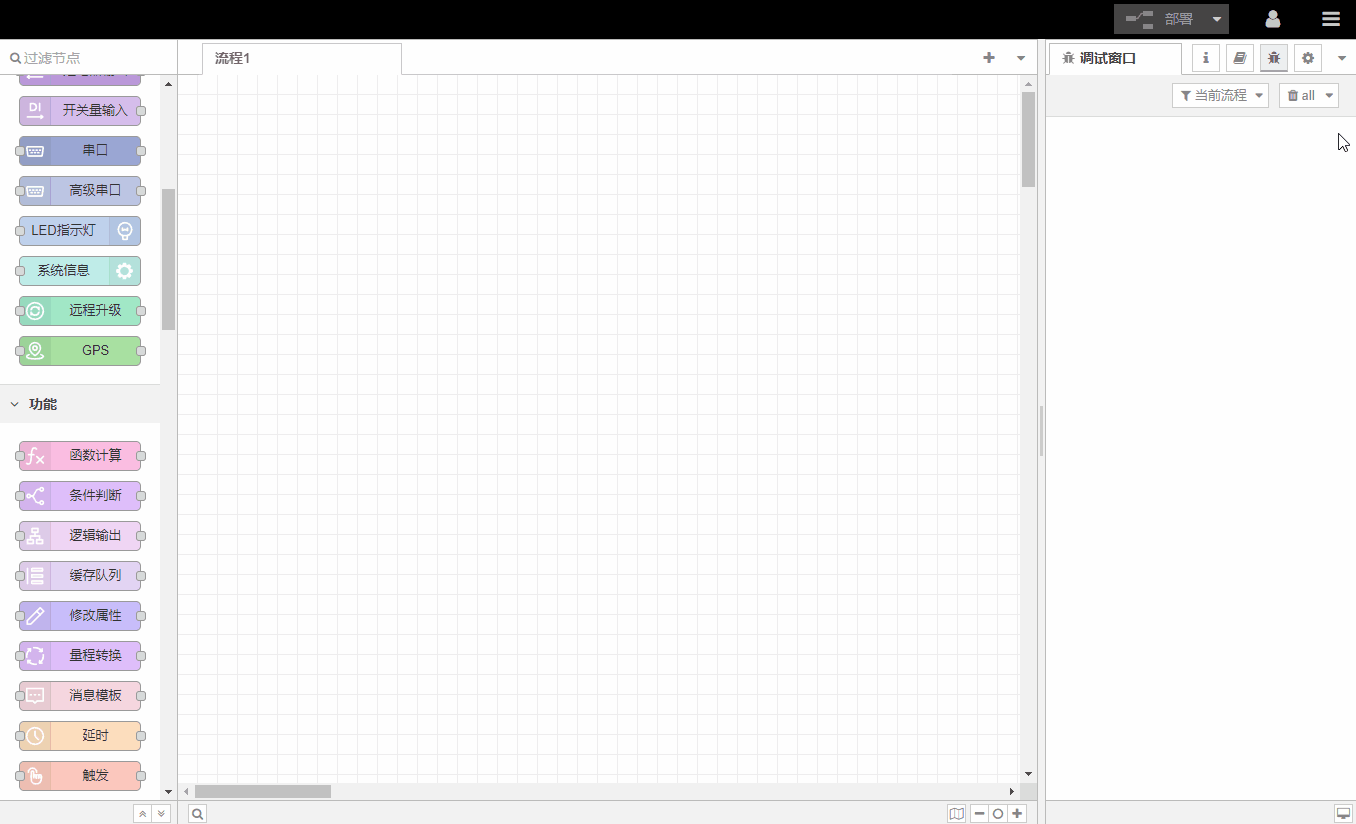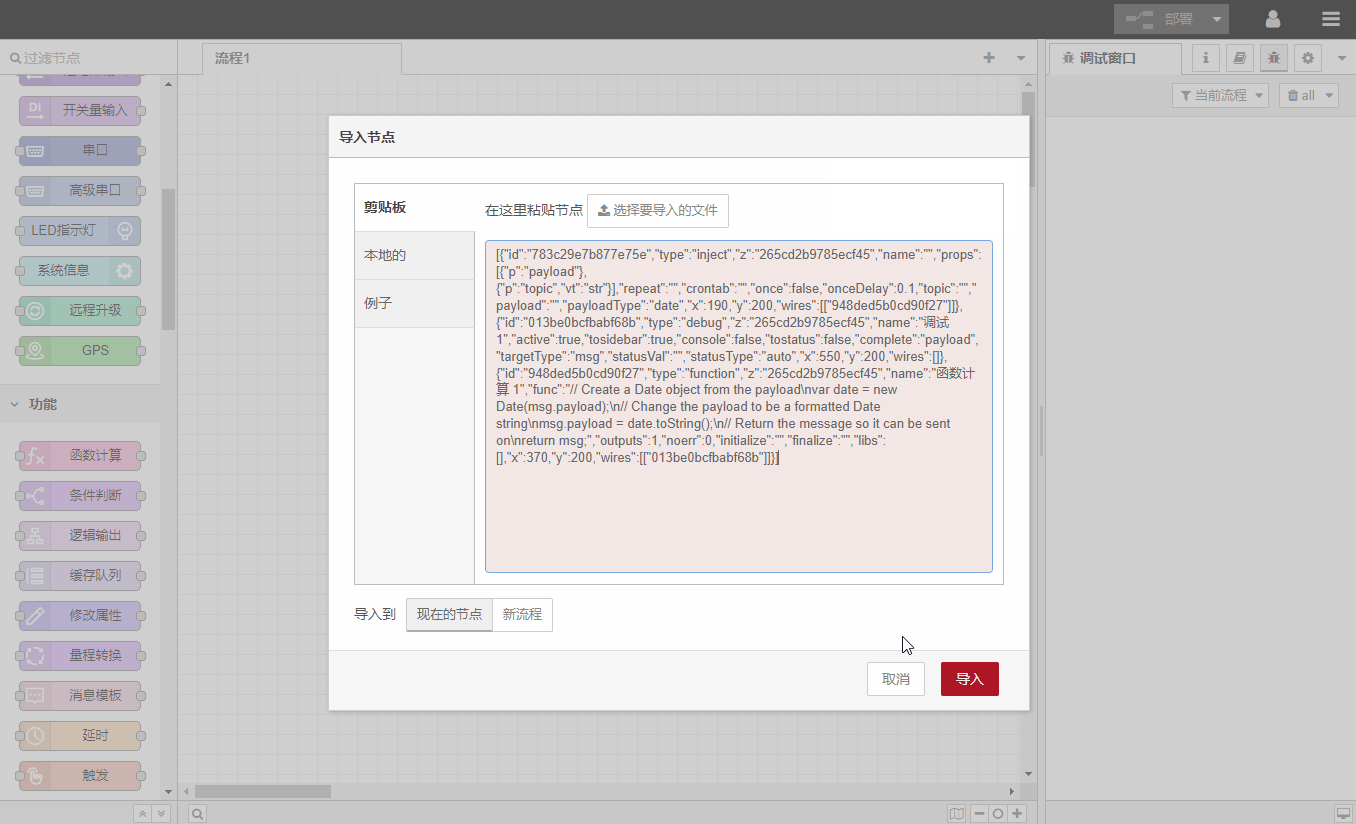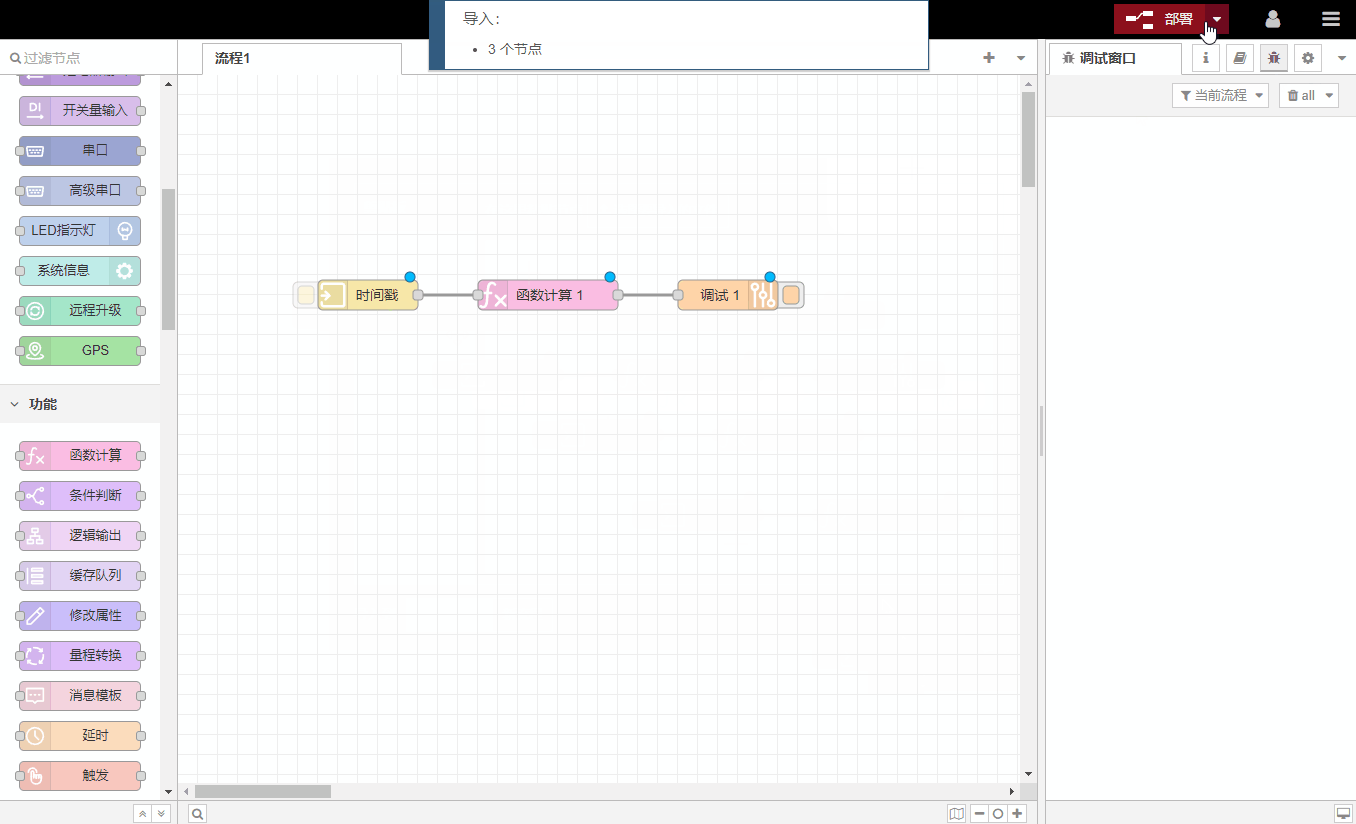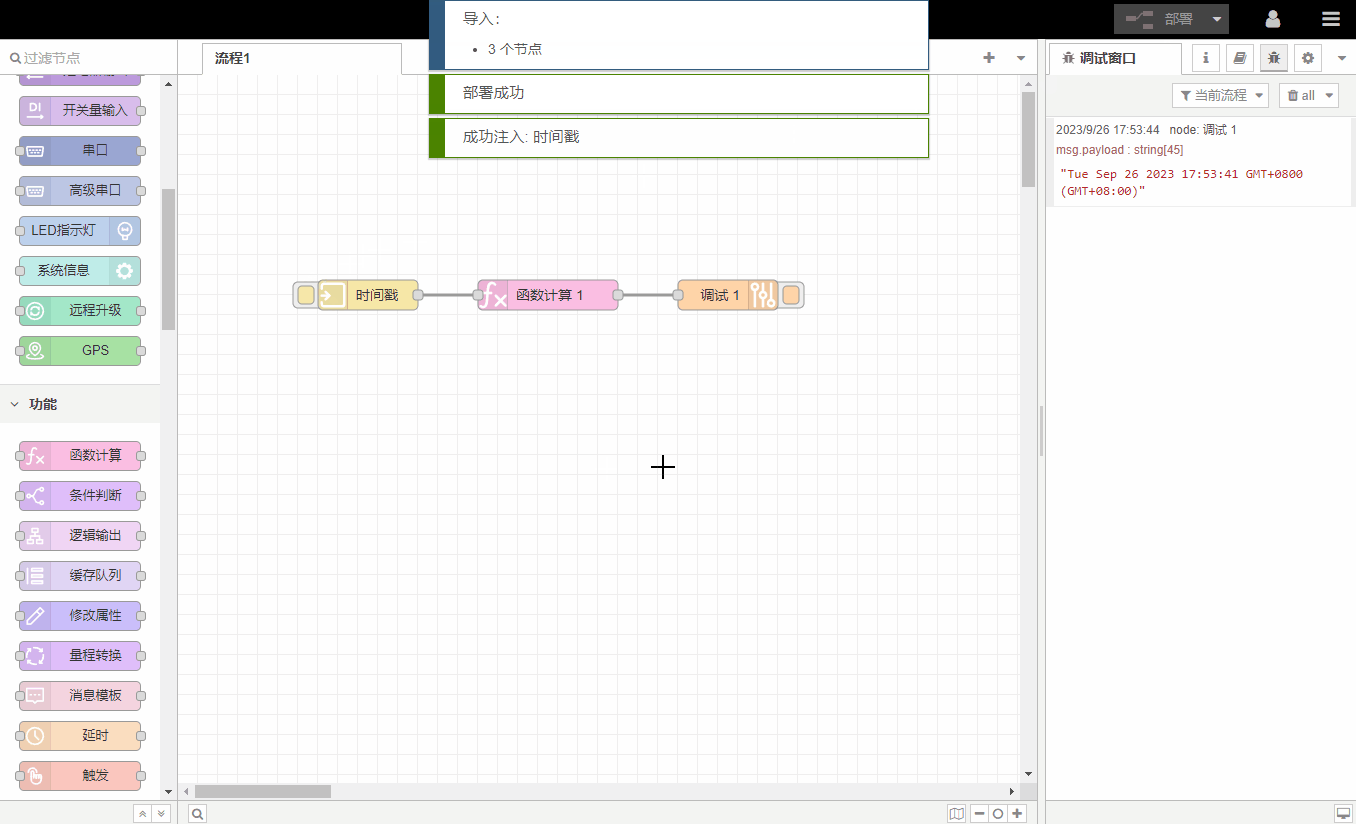
All processes support import and export in json format, making it easy to share completed processes with others.
Import: Supports the following methods to import the process
Copy JSON data directly
Upload JSON file
Browse the processes pre-installed in the gateway
Export: Supports the following methods to export the process
Generate JSON format data stream
Save it as JSON file
Keep it inside the gateway (not recommended)
debugging area
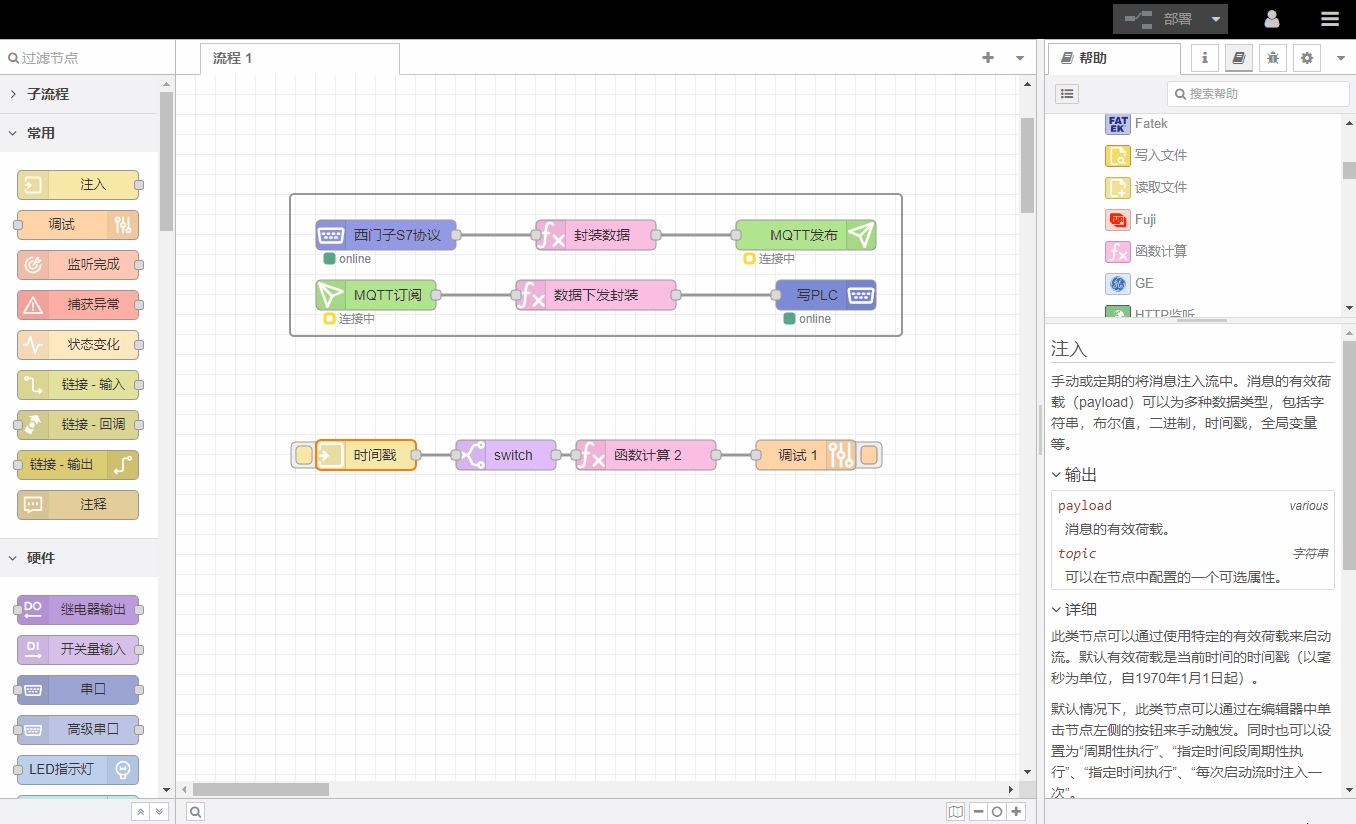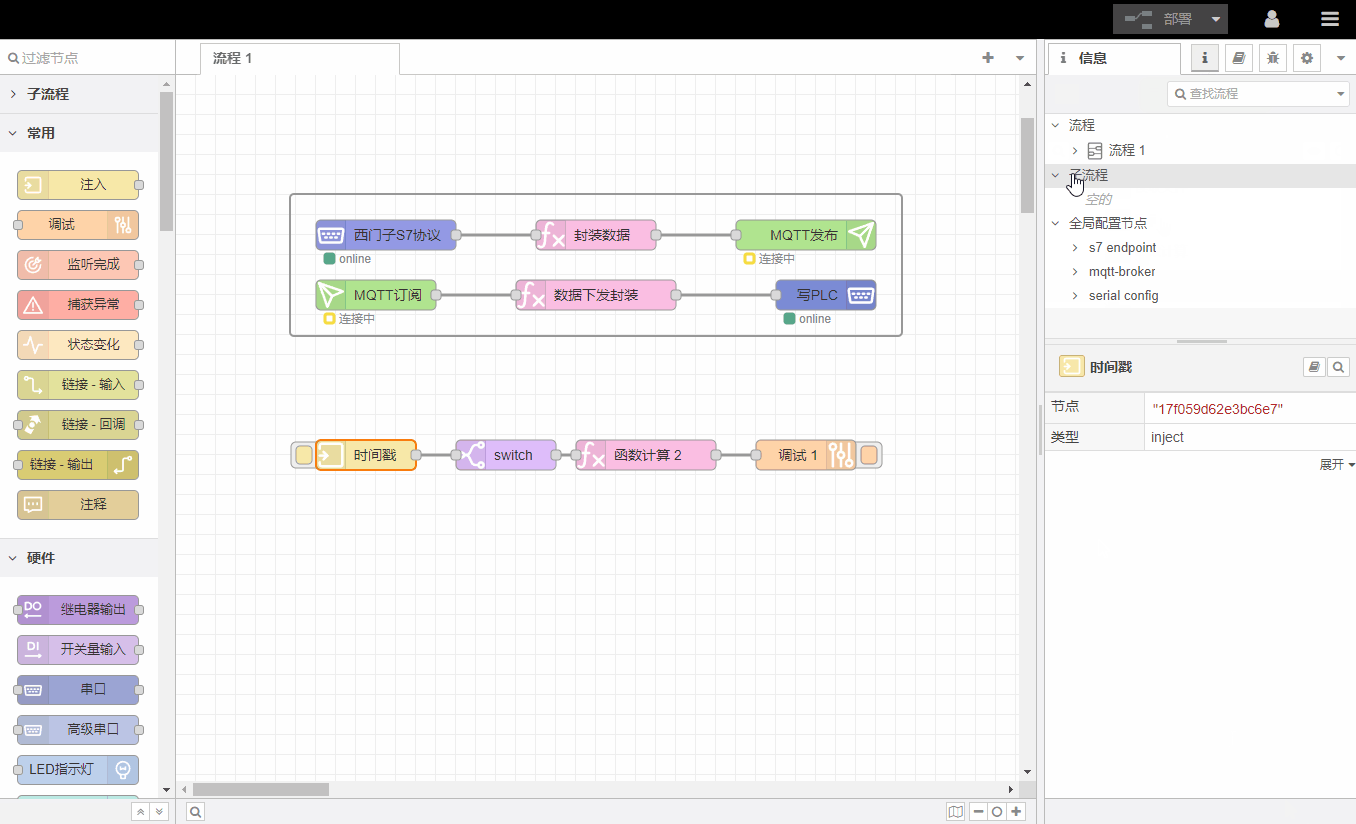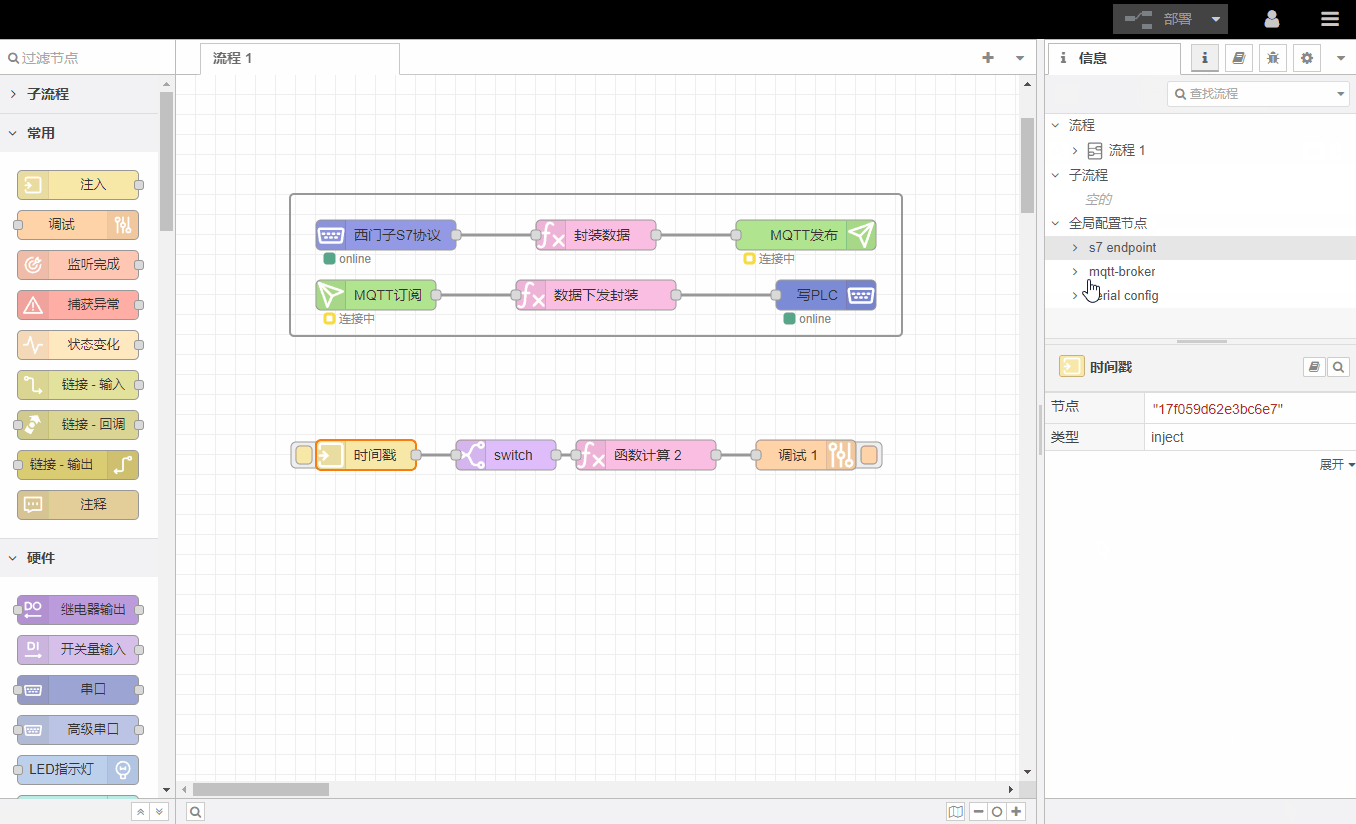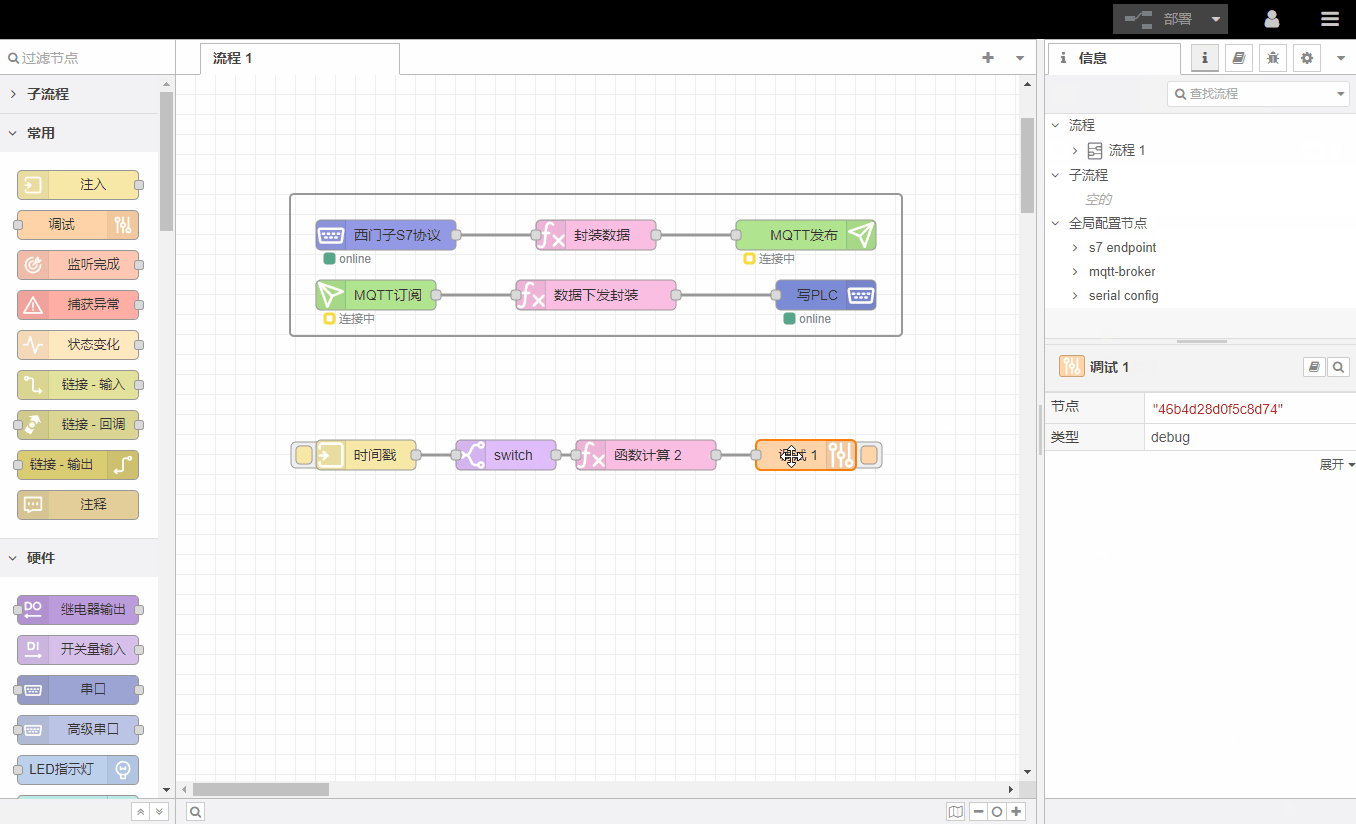
1.Information window
Information windows show information about a process or node, including an outline view of all processes and nodes, and details about the current selection
2. Help documentation
The help document window provides usage instructions for the currently selected node, please read it carefully.

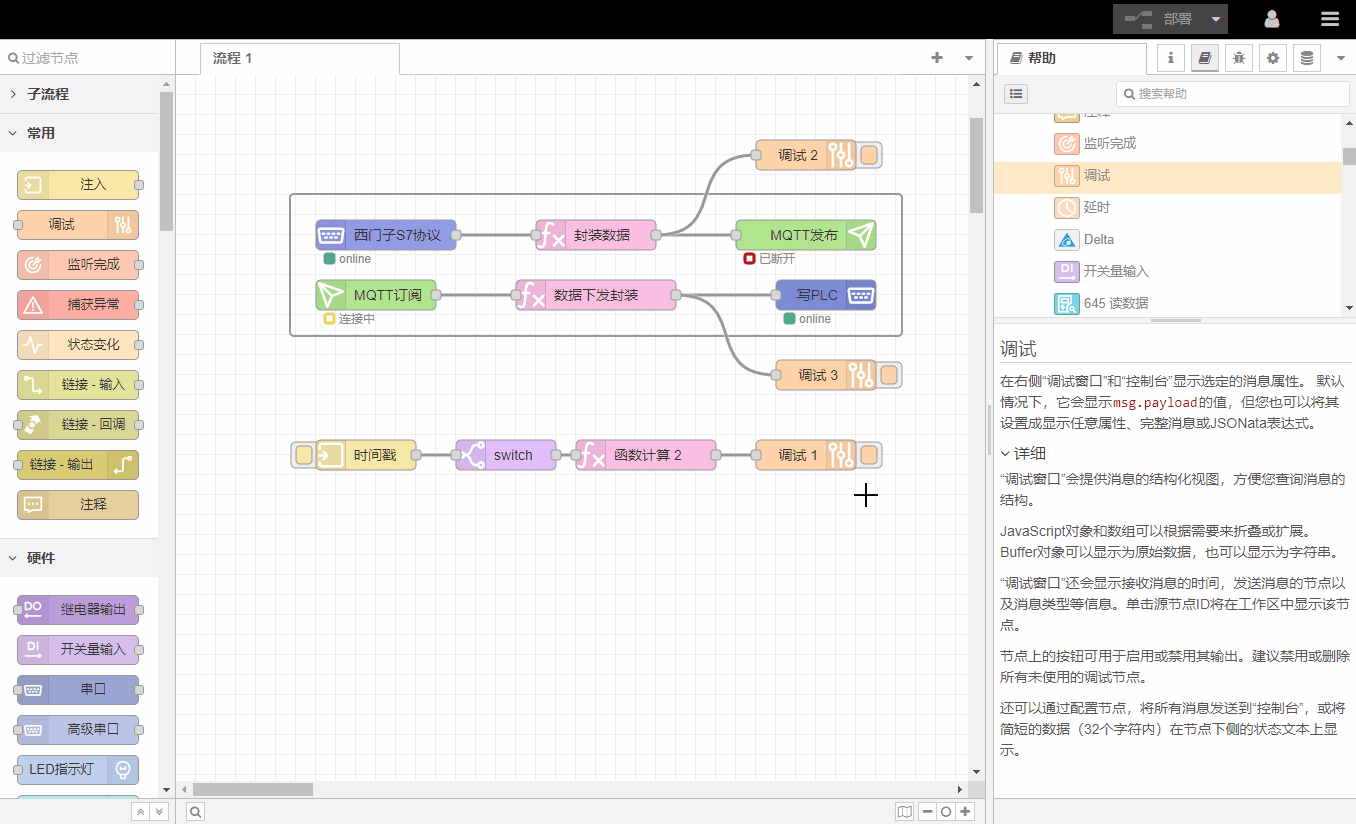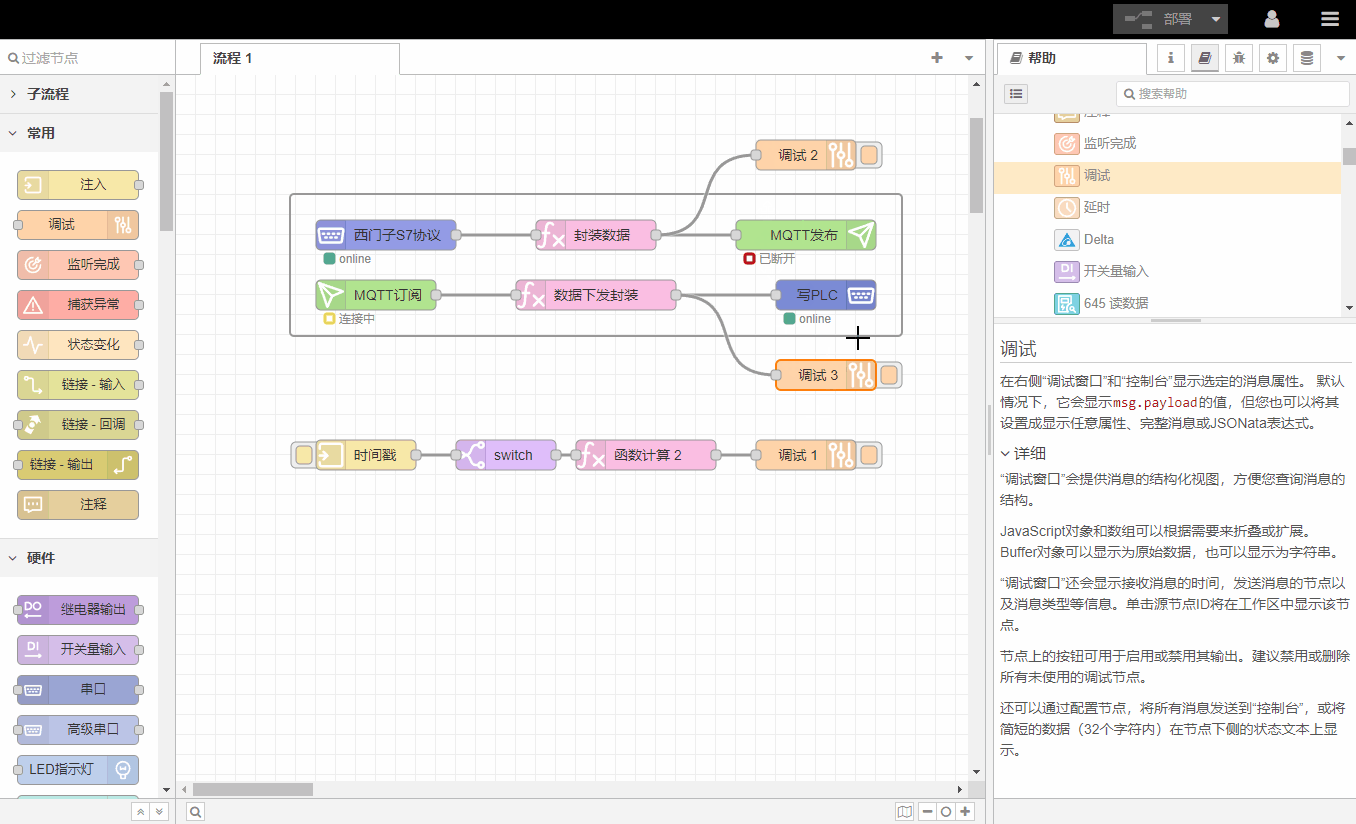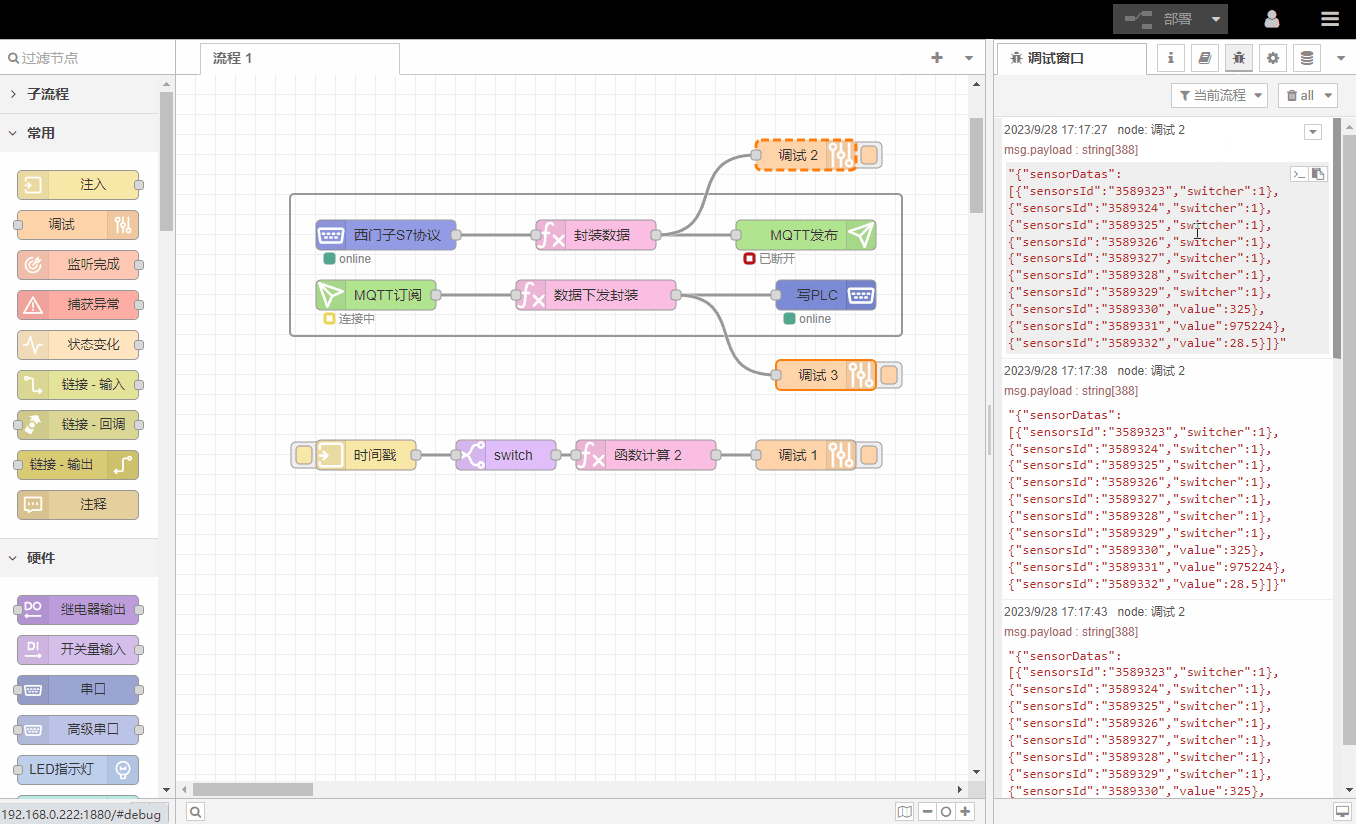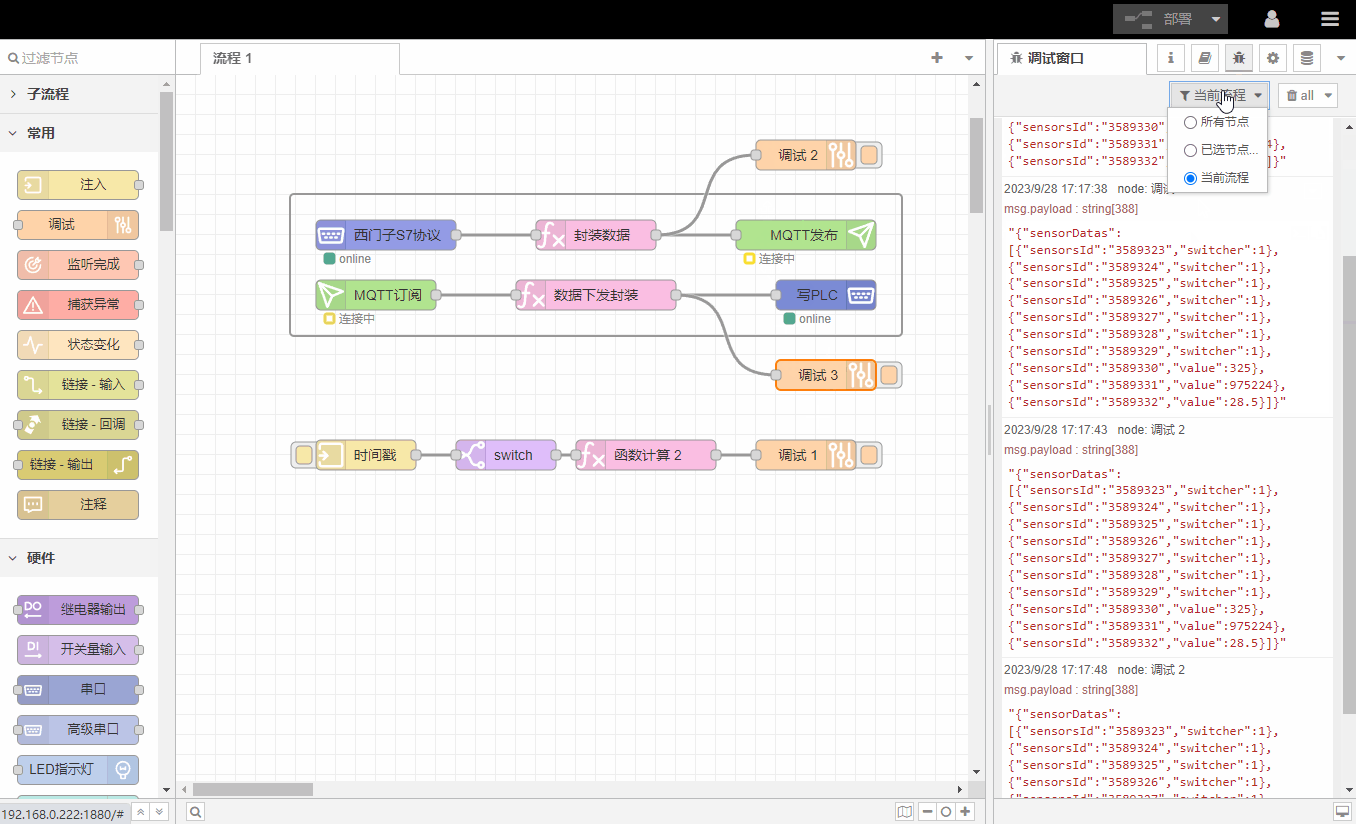
3.Log window
The log window displays all information received by 调试节点to facilitate debugging and problem location.
4. Configure nodes
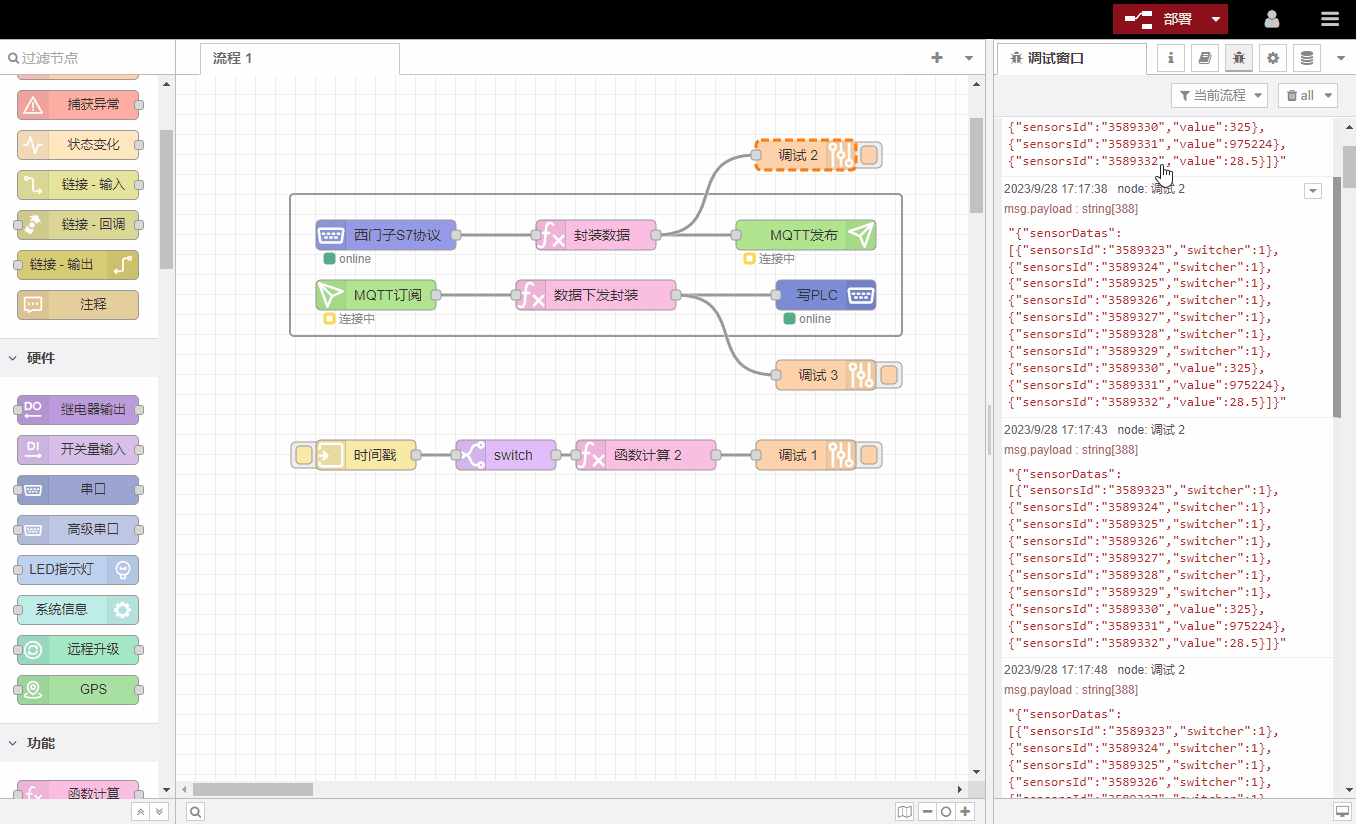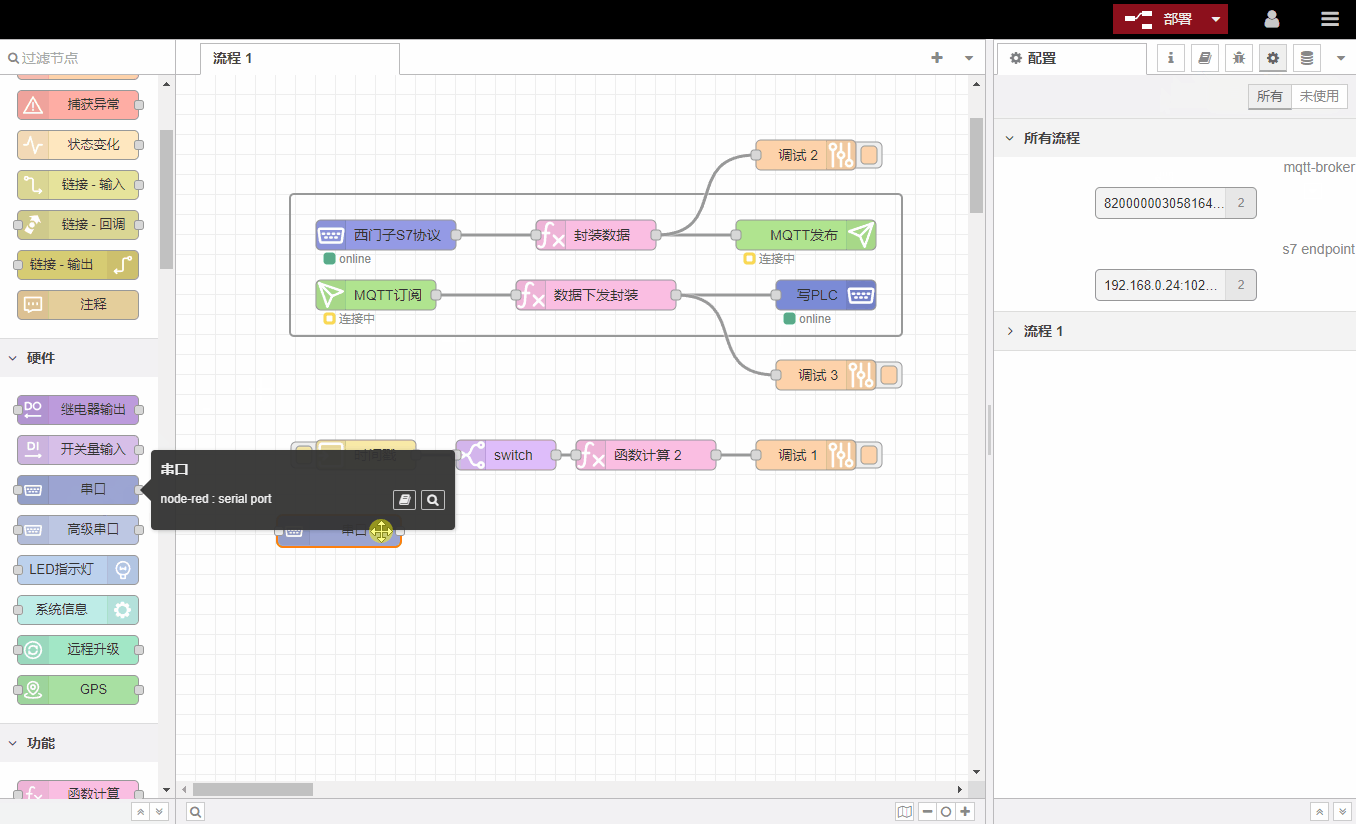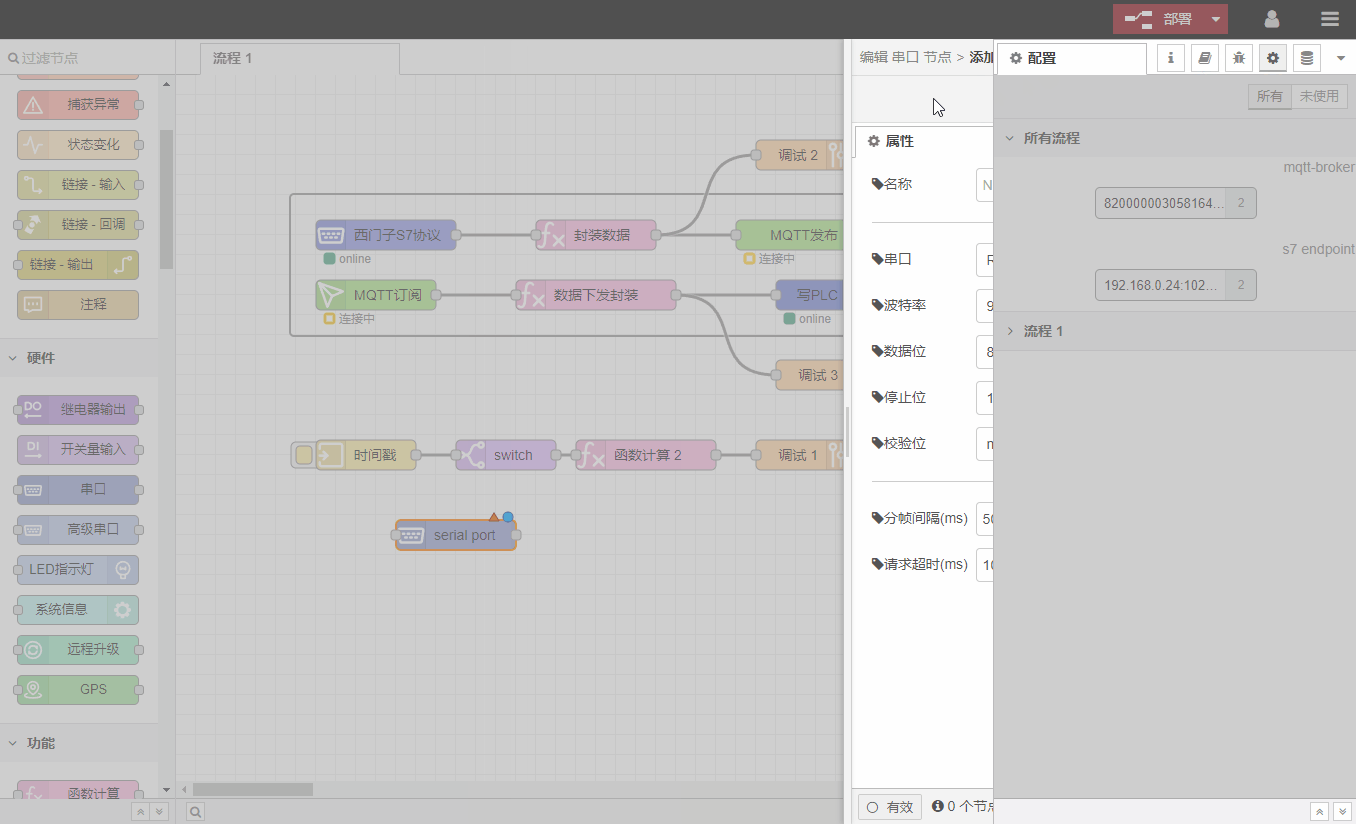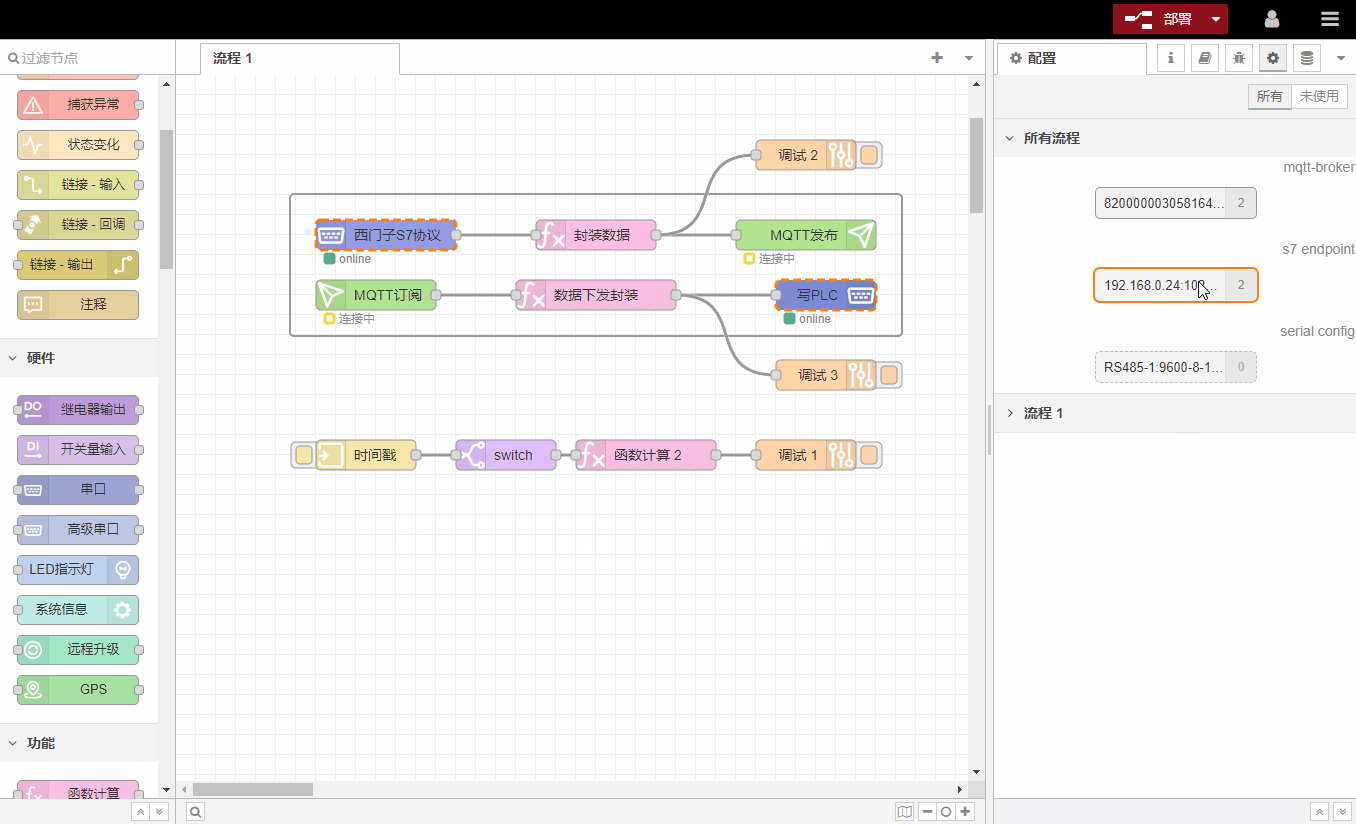
The configuration node window displays all configuration nodes that exist in the current process. Unused configuration nodes are displayed with dotted lines. After selecting, press the Delete key to delete the configuration node.
5.Global variables
The global variables window can view the currently used global variables, and click manually to refresh the latest values.